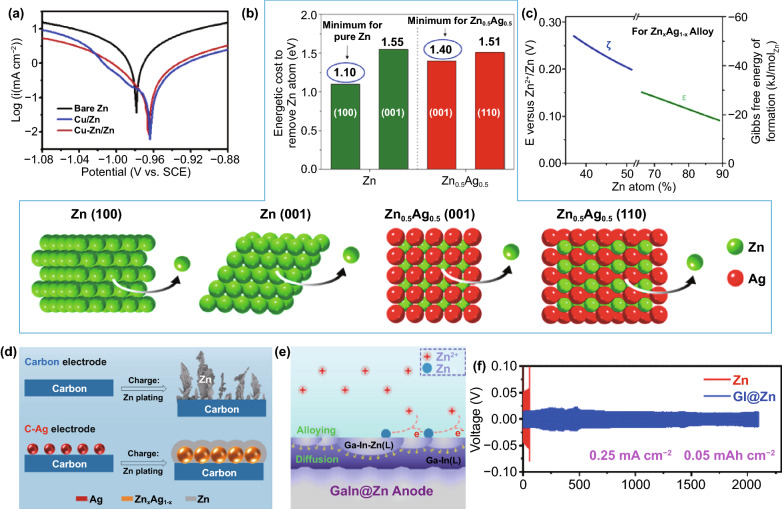
Fig. 13.
a Linear polarization curve of Cu/Zn and Cu–Zn/Zn electrode in 3 M ZnSO4 electrolyte [119].
Copyright 2020, Elsevier. b DFT simulation results showing the energetic cost of removing a Zn atom from the pure Zn metal and Zn0.5Ag0.5 alloy. Constructed models: Zn with 001 and 100 surfaces; Zn0.5Ag0.5 with 110 and 001 surfaces; c Calculated Gibbs free energy of formation at room temperature of Zn, ζ- and ε-ZnxAg1−x alloy phases and the corresponding electrochemical potential shift of Zn2+/ZnxAg1−x compared with that of Zn2+/Zn. d Schematic of Zn deposition on the (top) carbon paper substrate and (bottom) carbon paper slurry coated with Ag nanoparticles [121]. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society. e Dendrite-free GaIn@Zn anode by alloying–diffusion synergistic strategy; f Voltage profiles of symmetric cells using bare Zn foil and GaIn@Zn at a current density of 0.25 mA cm−2 [116]. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society