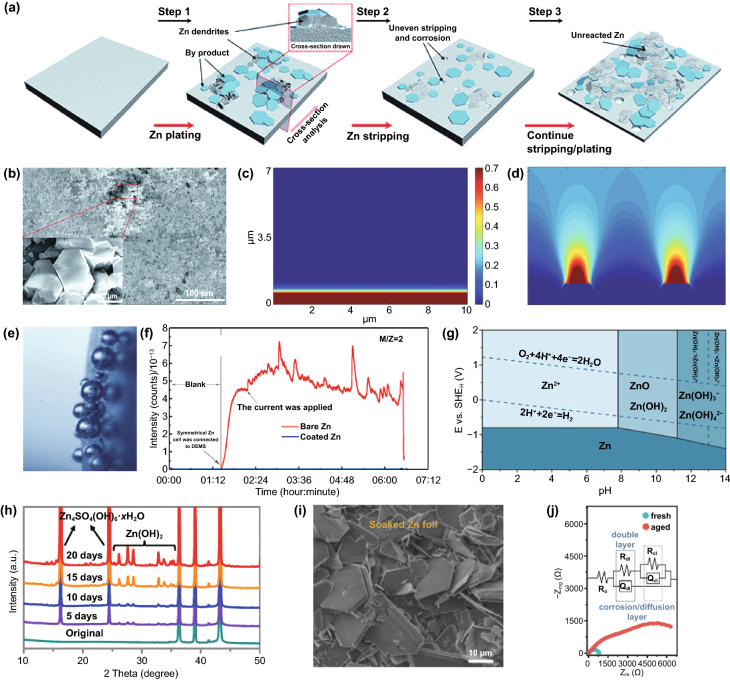
Fig. 2.
a Schematic illustration of the formation of inactive Zn; b Top-view SEM image of the Zn electrode after short circuit. Inset: flake-like dendrites [137].
Copyright 2021, Royal Society of Chemistry. Simulation of the diffusion and distribution of Zn ions along the 2D surface of the electrode with the conditions of c a flat surface and d 2 large dendritic seeds [29]. Copyright 2019, Wiley–VCH. e In situ optical microscope images of H2 gas evolution during the Zn electrodeposition process at 0.2 mA cm−2 [42]. Copyright 2019, Elsevier. f Online DEMS data for symmetrical Zn batteries with the bare Zn in 2 M ZnSO4 electrolyte, reflecting the hydrogen evolution of the anode during rest and charging/discharging process [43]. Copyright 2019, Royal Society of Chemistry. g Pourbaix diagram of ZnSO4–H2O system at 25 °C [44]. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society. h The in situ XRD patterns of bare Zn immersed in 2 M ZnSO4 electrolyte [48]. Copyright 2021, Wiley–VCH. i SEM image of Zn foil after soaking in 1 M ZnSO4 electrolyte for 7 days [41]. Copyright 2020, Wiley–VCH. j Nyquist plots of the fresh and aged Zn electrode. The inset shows the equivalent circuit [49]. Copyright 2021, Wiley–VCH