Figure 2. Production and characterization of aptamer-engineered NK cells (ApEn-NKs).
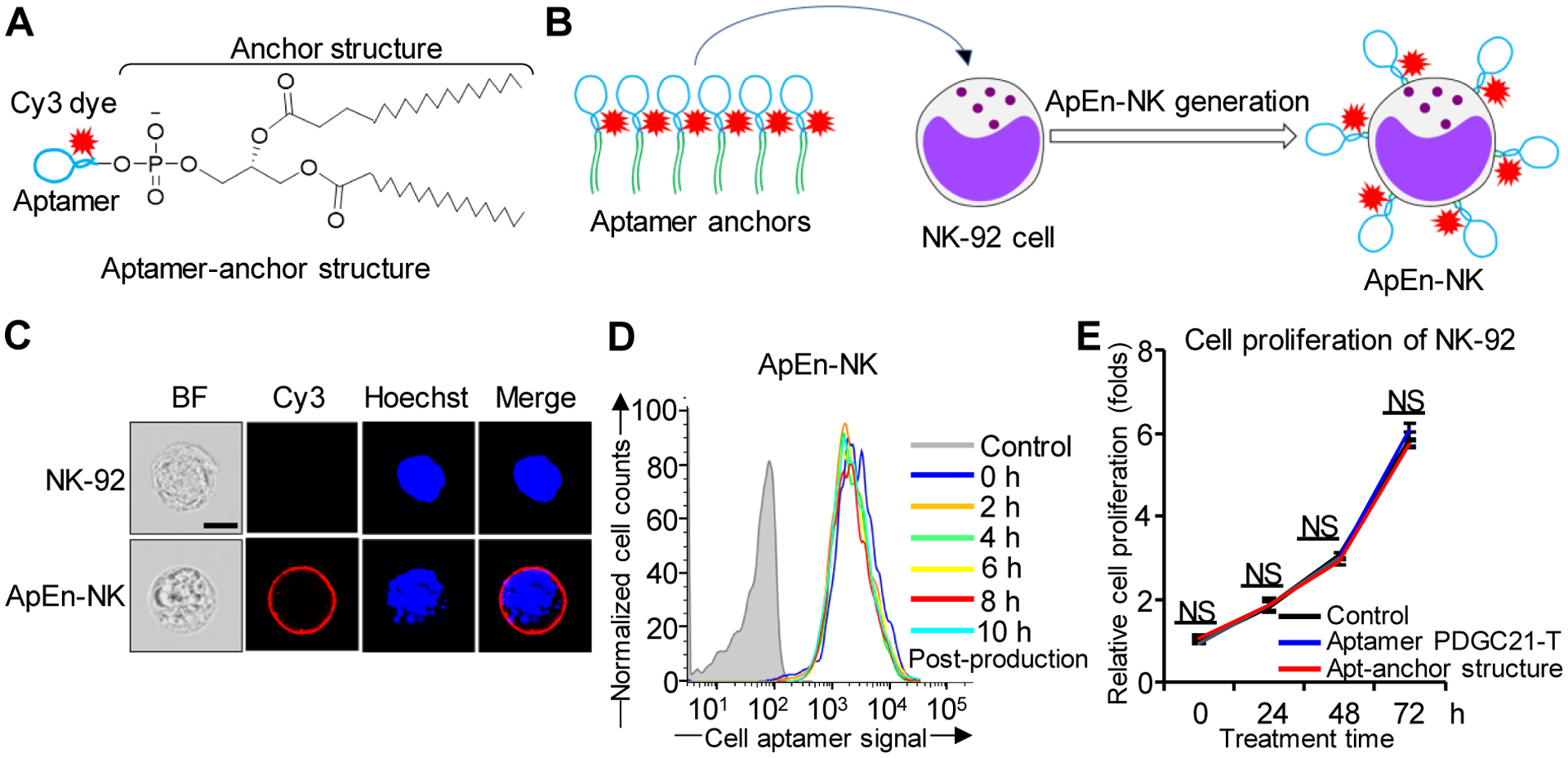
(A) Aptamer-anchor structures were formulated by conjugating the aptamer PDGC21-T sequence to two C18 anchor structures. (B) ApEn-NKs were produced by simple incubation of NK-92 cells with synthetic aptamer-anchor structures. (C) Confocal microscopy showed intact morphology of parental NK-92 cells (top) and fluorescent signal (red) derived from surface engineered aptamers on ApEn-NK (bottom). For tracking purposes, cell nuclei were stained with Hoechst dye (blue). Scale bar: 10 μm. (D) Stability assay of ApEn-NK products. No changes in fluorescent signals of surface-engineered aptamers on ApEn-NK were detected by flow cytometry analysis 10 h post-production. (E) Cell proliferation assay. The presence of aptamer alone or the aptamer-anchor structure to form ApEn-NK had no effect on NK-92 cell proliferation 72 h post incubation. NS: not significant.
