Figure 7. ApEn-NK treatment inhibits tumor nodule formation of lung metastasis in TNBC xenograft mice.
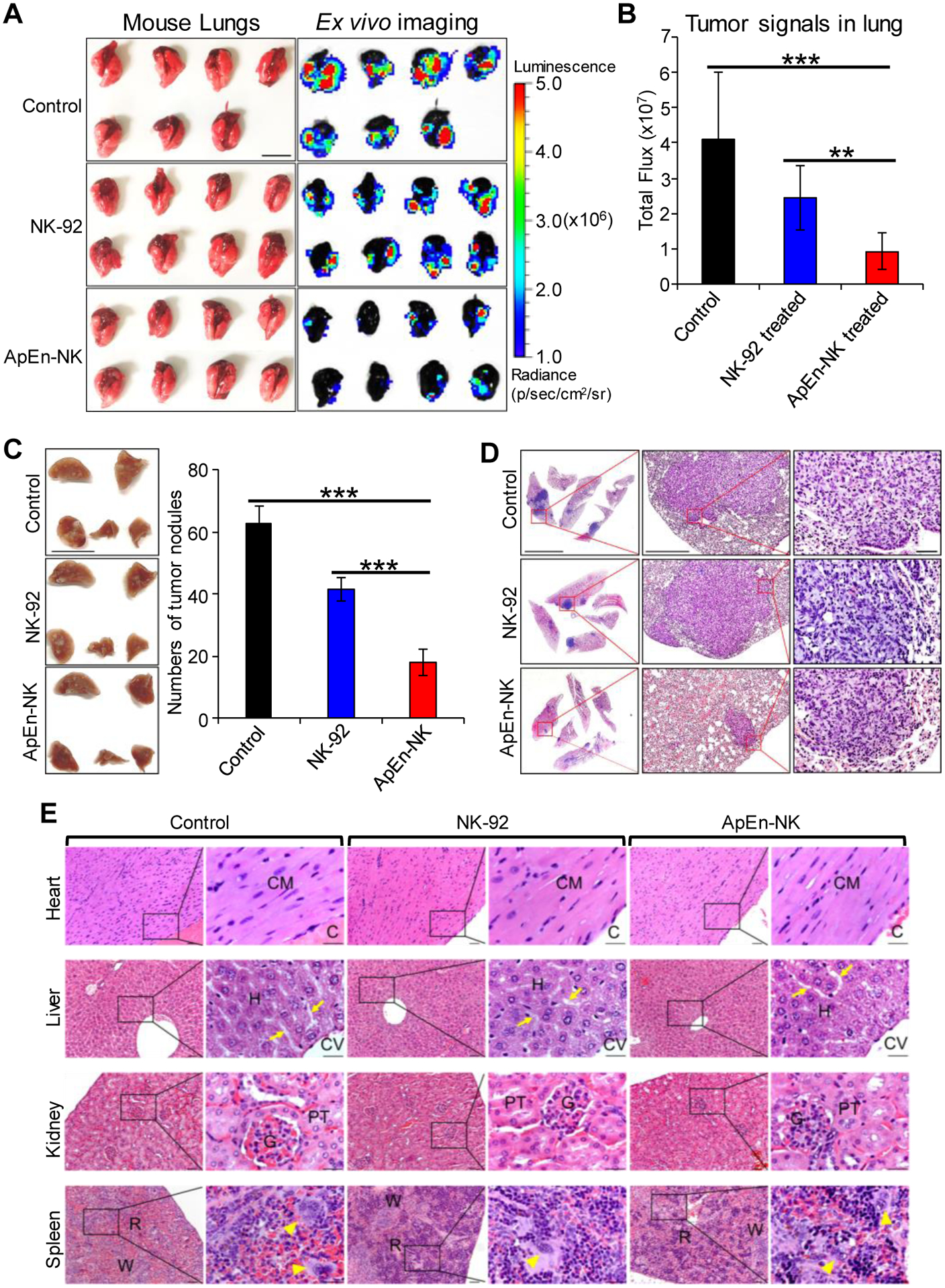
(A) Ex vivo imaging of lung tissues performed immediately following the whole-body imaging study at the study endpoint. Luminescence radiance is displayed as photons/second/square centimeter/steradian. Scale bar: 1 cm. (B) Tumor signals derived from lung metastasis in mice with different treatments. (C) Tumor nodules of metastasis in fixed lung tissues were counted using a stereomicroscope under 10X magnification. Scale bar: 1 cm. (D) Hematoxylin and Eosin staining of tumor nodules derived from TNBC cells at 10X (left), 40X (middle), and 200X magnification (right). Data are presented as mean ± S.D. **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001 (Student’s t-test, two-tailed). NS: not significant. Scale bars from left to right: 5 mm, 0.5 mm, 0.05 mm. (E) ApEn-NK had no side toxicity to mouse normal tissues. Major organs (heart, liver, kidney, and spleen) were collected at experiment endpoint from mice different treatments as indicated. Histology examination was performed under a microscope with 100X and 400X magnification. No morphological abnormalities were detected in mouse major organs. (CM = Cardiac myocyte; C = Cardiac cavity; H =Hepatocyte; CV = Central vein; P = Portal area. Arrow = Hepatic sinusoid; G = Glomerulus; PT = Proximal tubule; R = Red pulp; W = White pulp; Arrowhead = Megakaryocyte. Scale bar of low and high magnification were 0.05 mm and 0.025 mm, respectively.
