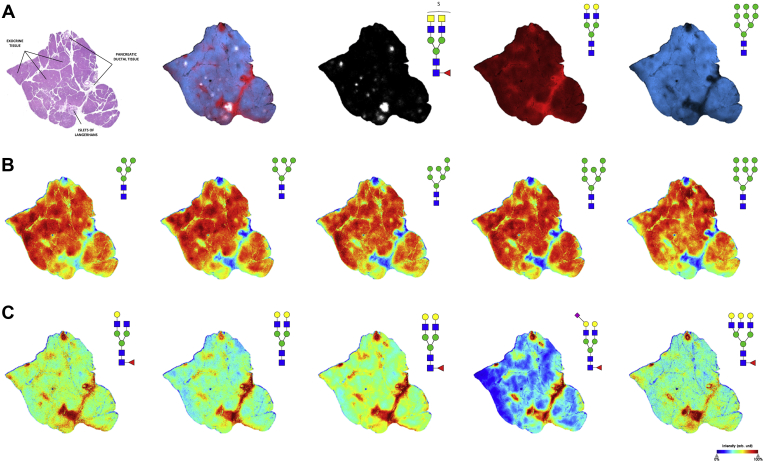
Fig. 1.
N-glycan imaging of a normal human pancreas.A, the overlay image of three representative N-glycans corresponding to acinar exocrine tissue (blue, Hex9HexNAc2 m/z 1905.6338), ductal tissue (red, Hex5HexNAc4 m/z 1663.5814), and islets of Langerhans (white, Hex3dHex1HexNAc6SO42 m/z 1993.6390) along with accompanying annotated H&E stain. B, high-mannose N-glycans predominantly localized to acinar exocrine tissue. C, N-glycans expressed predominantly in pancreatic ductal tissue tend to be biantennary and triantennary structures with core fucose residues lacking terminal fucosylation.