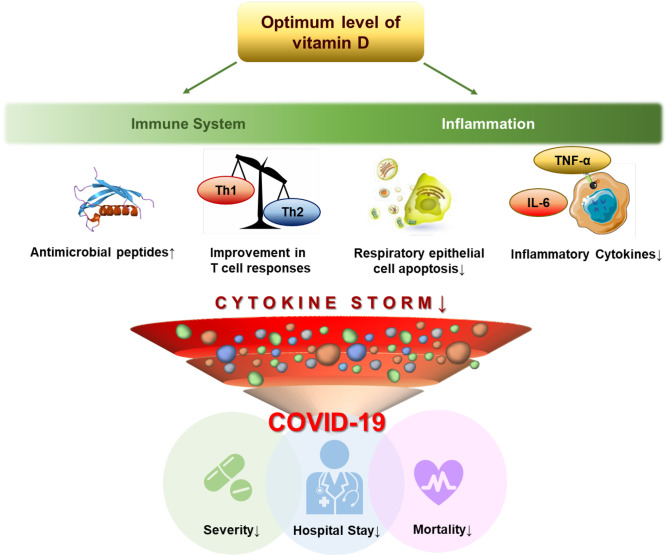
Fig. 3.
Potential effects of optimum levels of vitamin D on critical pathways involved in the progress of COVID-19. COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; IL-6, interleukin-6; Th1, type 1 helper T cell; Th2, type 2 helper T cell; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α. References for evidence: antimicrobial peptides [36]; T cell responses [43]; apoptosis of infected respiratory epithelial cells [150]; and inflammatory cytokines [58]