Fig. 7.
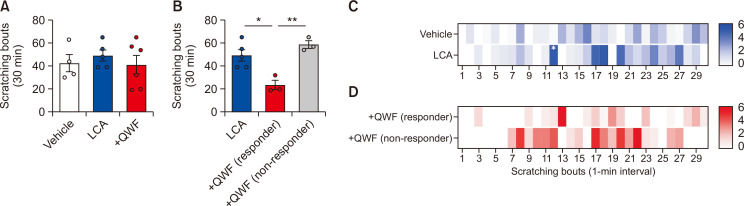
Lithocholic acid (LCA) induces mild scratching behavior in both cheek models. (A) Intradermal injection of LCA into the cheek (50 µg/site, n=5) did not induce significant changes in total bouts of scratching compared to vehicle (n=5). Additionally, co-administration of LCA and QWF (500 µM, n=6) did not affect the total bouts of scratching. (B) QWF induced mixed responses in mice when co-treated with LCA, resulting in decreased scratching bouts in one group (responder) or no responses in the other group (non-responder). Heatmap data of scathing bouts per 1-min interval showing the time course of scratching behavior induced by intradermal injection of LCA alone (C) or co-treatment with QWF (D). Different scratching profiles among groups, which are not easily detected when the data are only presented as total bouts of scratching. *p<0.05.