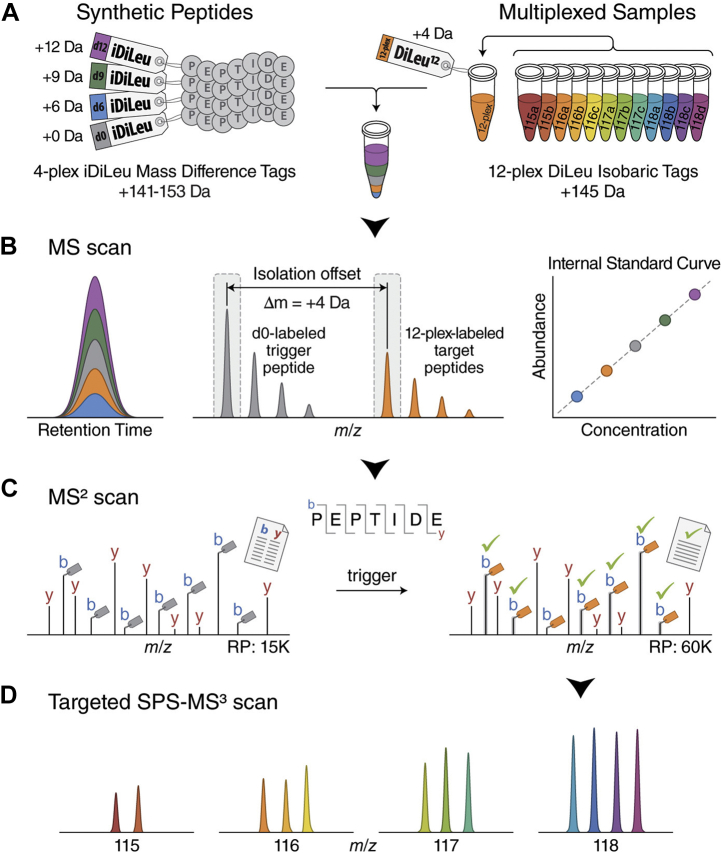
Fig. 5.
Schematic illustration for the HOTMAQ method.A, synthetic peptides are labeled with four-plex iDiLeu at different concentrations and spiked into 12-plex DiLeu-labeled analytes. B, labeled peptides are detected with identical chromatographic elution profiles as five precursor ion clusters. The iDiLeu labeled-synthetic peptides are used to generate internal calibration curves to quantify the total amount of multiplexed target peptides. iDiLeu d0-labeled synthetic trigger peptides and multiplexed DiLeu-labeled target peptides are separated in MS1 spectra by a mass offset of 4.01 Da, which enables synthetic trigger peptides to initiate quantitative analysis of target peptides via MS2 regardless of target peptide precursor abundances. C, real-time MS2 analysis of d0-labeled synthetic peptides by matching MS2 spectrum to a product mass inclusion list unambiguously triggers fragmentation of 12-plex DiLeu-labeled target peptides in a predefined monitoring window. Acquisition parameters alternate between a low-resolution scan for monitoring d0-labeled trigger peptides and a high-resolution scan for quantifying 12-plex DiLeu-labeled target peptides. Fragment ions of 12-plex DiLeu-labeled target peptides are selected for synchronous precursor selection (SPS)-MS3 analysis. D, the relative abundance of each 12-plex DiLeu-labeled peptide is accurately determined by targeted SPS-MS3 acquisition at a resolving power of 60K (at m/z 200). The absolute amounts of target peptides are quantified by integrating the total amount obtained using the standard curve. Adapted from Zhong et al. (156) with permission.