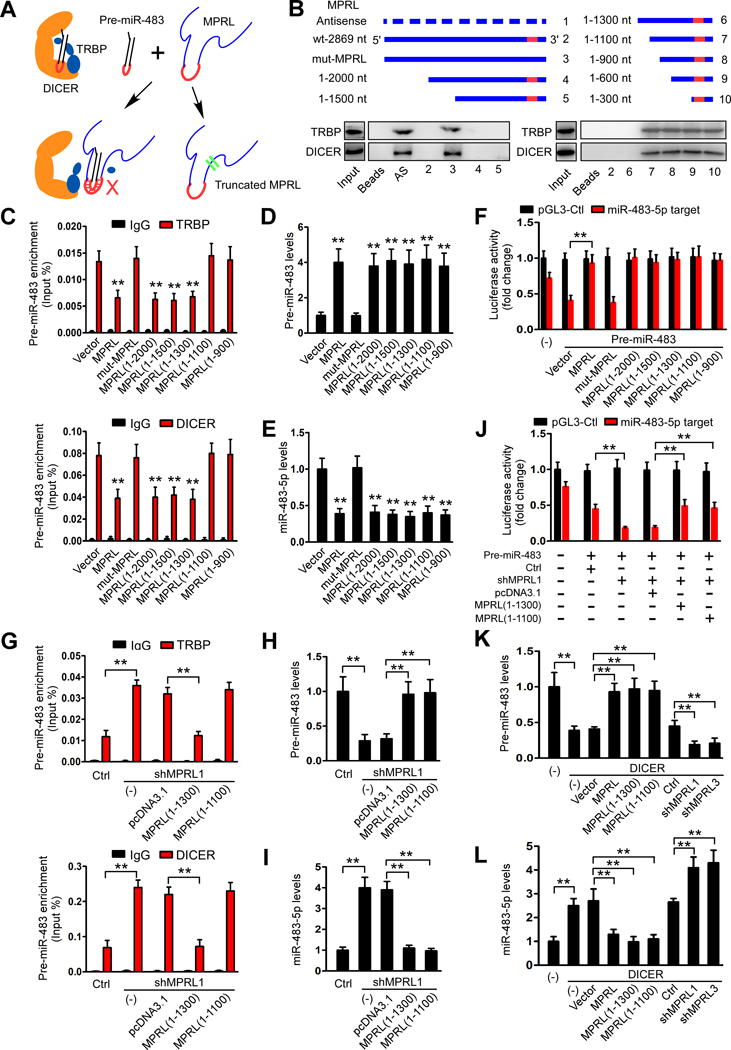
Figure 4. MPRL inhibits pre-miR-483 recognition and cleavage by the TRBP-DICER complex in CAL-27 cells.
(A) Schematic representation of inhibition of pre-miRNA recognition and cleavage by DICER-TRBP complex in the presence of MPRL. (B) Serial deletions of MPRL were used in RNA pull-down assays to identify valid length of MPRL that is required for physically masking the recognition of pre-miR-483 by the TRBP-DICER complex. (C) Site-directed mutagenesis of MPRL to 1100 nt resulted in the inability of MPRL to mask the recognition of pre-miR-483 by TRBP and DICER. (D and E) Overexpression of truncated isoforms of MPRL increased pre-miR-483 levels (D) and subsequently reduced miR-483–5p levels (E), while mutant MPRL (1–1100) had no effect. (F) Luciferase reporter assays showed that miR-483–5p function was inhibited by overexpression of truncated MPRL. (G) Forced expression of the truncated MPRL (1–1300) but not the MPRL (1–1100) abolished the increase in pre-miR-483 immunoprecipitated with TRBP and DICER by depletion of endogenous MPRL. (H and I) Overexpression of MPRL (1–1300) and MPRL (1–1100) increased pre-miR-483 levels (H) and reduced miR-483–5p levels (I). (J) Luciferase reporter assays demonstrated that MPRL(1–1300) and MPRL(1–1100) overexpression abolished the increase in miR-483–5p functionality by MPRL depletion. (K-L) qRT-PCR demonstrated that overexpressing MPRL or the truncated isoforms (1–1300) and (1–1100) prevented the reduction in pre-miR-484 (K) and attenuated the increase in miR-483–5p (L) induced by DICER, while silencing MPRL had the opposite effects. *P<0.01 and **P<0.001, 1-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s tests for multiple comparisons.