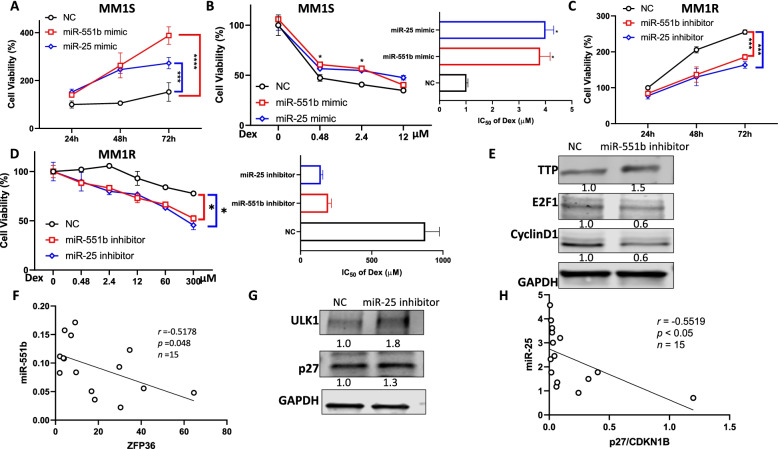
Fig. 4.
MiR-551b and miR-25 level affect Dex sensitivity in MM. A Overexpression of miR-551b and miR-25 increases cell proliferation and (B) decreases cell sensitivity to Dex treatment in MM1S cells. (C) Knockdown of miR-551b and miR-25 expression inhibits cell proliferation and (D) increases sensitivity to Dex in MM1R cells. MM1S cells were transfected with microRNAs: miR-551b mimic, miR-25 mimic or non-targeting control (NC), MM1R cells were transfected with anti-miRs: miR-551b inhibitor, miR-25 inhibitor or non-targeting control (NC). Cell proliferation was measured at 24 h, 48 h and 72 h. Transfected cells were treated Dex at indicated concentration for 48 h. Cell viability was measured and IC50 values of Dex were calculated using GraphPad Prism 8 and shown in the right panels. Data were analyzed using unpaired Student t tests: Data presented as mean ± SD. ns, not significant; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. E Knockdown of miR-551b expression increased TTP protein level and decreased E2F1 and CyclinD1 in MM1R cells. F miR-551b level negatively correlates with ZFP36 level in in 15 primary MM samples. ZFP36 mRNA expression was assessed by q-PCR and presented as relative level normalized to GAPDH. MiR-551b level was measured by Taqman q-PCR and presented as relative level normalized to RNUB. Pearson correlation analysis was performed. p and r values were labeled. G Knockdown of miR-25 expression increased protein levels of ULK1and p27 in MM1R cells. H miR-25 level negatively correlates with p27/CDKN1B level in in 15 primary MM samples