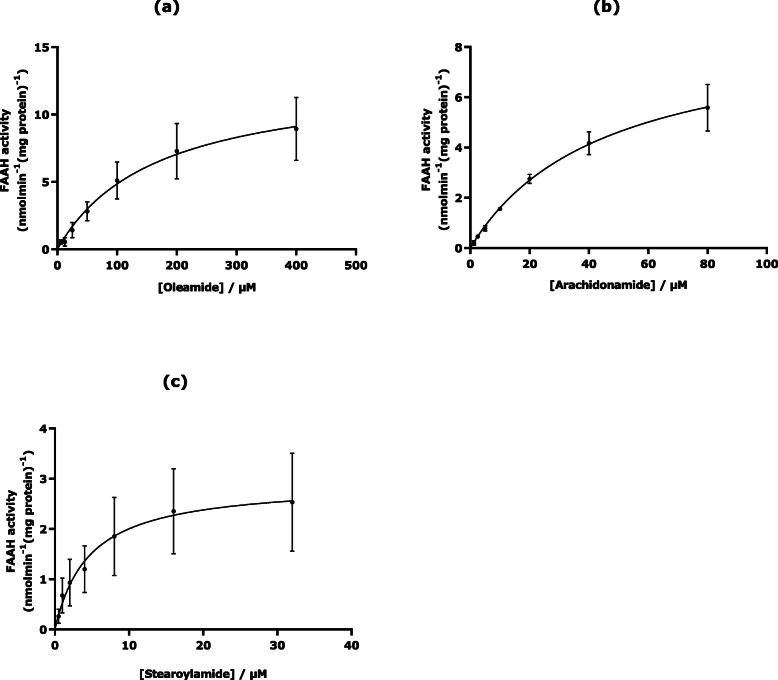
Fig. 1.
Hydrolysis of oleamide (a), arachidonamide (b) and stearoylamide (c) by rat liver FAAH-1 activity. Rat liver FAAH-hydrolytic activity of each primary amide substrate in vitro, was assayed by quantification of ammonia released after hydrolysis. Ammonia generated in the presence of sulphite ions is reacted with alkaline o-phthaldehyde (OPA) to generate the stable fluorescent isoindole derivative (1-sulphonatoisoindole) which is quantified by fluorescent spectroscopy [41, 43]. Four separate experiments with three replicates on the same microtiter plate were conducted for each substrate using different rat liver preparations. Data are mean ± SEM (Standard Error of the Mean) of four separate preparations (n = 4) conducted in triplicate