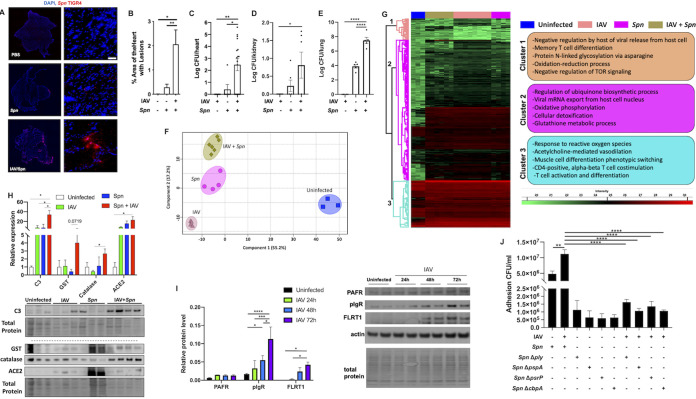
FIG 1.
Primary pandemic influenza virus infection promotes S. pneumoniae translocation to the heart, upregulation of adhesion factors, and global proteome remodeling. Male and female 6- to 8-week-old C57BL/6N mice were intranasally infected with A/California/7/2009 (IAV) at day 0. At day 10, mice were infected with S. pneumoniae intratracheally at a dose of 1 × 103 CFU. Mice were euthanized, and heart tissue was collected at day 12. (A) Immunofluorescent staining for S. pneumoniae capsule (red) in cardiac tissue sections. Cell nucleus was stained in blue. White bar, 50 μm. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. (B) Percentage of area of heart with lesions was measured using ImageJ. Bacterial titers (in log CFU) in homogenized hearts (C), kidneys (D), and lungs (E) upon euthanasia. (F and G) Principal-component analysis (PCA) (F) and hierarchical clustering (G) of LFQ intensities of significantly changed proteins (ANOVA, FDR of 0.05) among uninfected, IAV-infected, S. pneumoniae-infected, and IAV and S. pneumoniae-infected hearts. Enriched GO biological process terms are indicated for marked clusters. (H) Immunoblots for complement C3 (C3), catalase, GST, and ACE2. (I) Immunoblots for complement PAFr, pIgR, and FLRT1. Protein level quantification was performed using ImageJ. (J) Adhesion assay CFU/mL of cells infected with or without IAV at an MOI of 2 for 2 h and then challenged with S. pneumoniae WT, Δply, ΔpspA, ΔpsrP, or ΔcbpA. Proteomic data are representative from 2 separate experiments done with 3 mice of each sex; no sex-based differences were observed. Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple-comparison posttest was performed. Asterisks denote the level of significance observed as follows: *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001; and ****, P ≤ 0.0001.