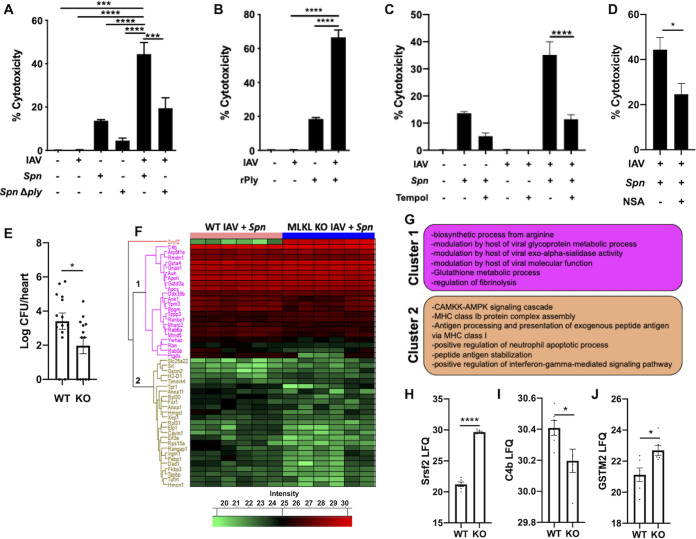
FIG 2.
Influenza virus infection potentiates pneumococcus-induced cardiomyocyte toxicity. (A and B) Cytotoxicity levels in AC16 cells infected with H1N1 at an MOI of 2 for 2 h and then challenged with S. pneumoniae or S. pneumoniae Δply at an MOI of 10 (A) or challenged with recombinant pneumolysin (0.3 μg) for 4 additional hours (B). (C and D) Cytotoxicity of cells after pretreatment for 1 h with superoxide dismutase mimetic, Tempol (10 μM) (C), or necrosulfonamide (10 μM) (D) and subsequently infected as described above. (E) Bacterial titers (in log CFU) in homogenized hearts of IAV/S. pneumoniae-infected hearts of WT C57BL/6 and MLKL KO mice upon euthanasia. (F) Hierarchical clustering of LFQ intensities of significantly changed proteins (ANOVA, FDR of 0.05) among IAV/S. pneumoniae-infected hearts of WT C57BL/6 and MLKL KO mice. (G) Enriched GO biological process terms are indicated for marked clusters. (H to J) Histograms of label-free quantitation-based intensity of Srsf2 (H), C4b (I), and GSTM2 (J). Student's t test or Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple-comparison posttest was performed. Asterisks denote the level of significance observed as follows: *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; and ***, P ≤ 0.001.