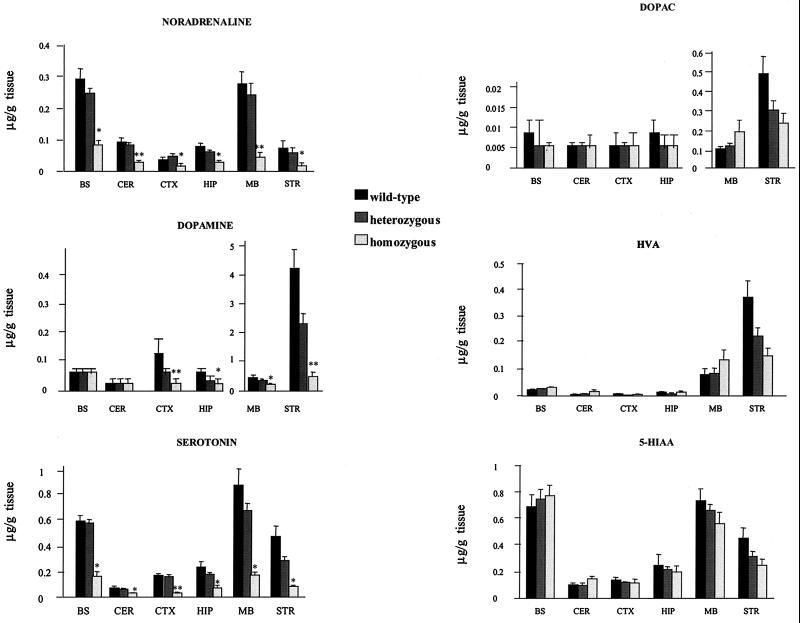
FIG. 4.
Quantification of monoamines and metabolites in different brain regions of wild-type, heterozygous, and homozygous mice. Dopamine, noradrenaline, and serotonin, as well as their main metabolites, DOPAC, HVA, and 5-HIAA, were measured in perchloric acid extracts prepared from brain areas of 13 wild-type, 17 heterozygous, and 6 homozygous mice using HPLC with electrochemical detection (12). In comparison to wild-type controls, KA1 homozygous mice showed widespread, major reductions in the levels of all three monoamines. The results are represented as the mean ± SEM. ∗, P < 0.05; ∗∗, P < 0.001, compared with the wild-type group (Student t test). In contrast, metabolite levels of all three monoamines were, in general, much less affected in the VMAT2-deficient KA1 mice, consistent with higher rates of monoamine turnover in these animals.