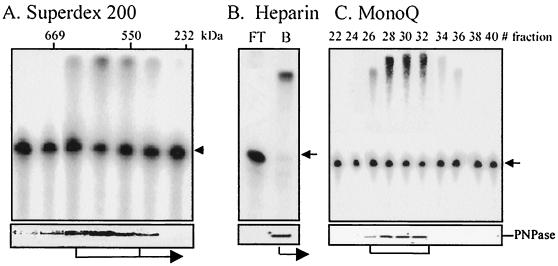
FIG. 2.
Copurification of PNPase and the RNA polymerization activity. (A) A chloroplast soluble protein extract was fractionated on a Superdex 200 size-exclusion column. Fractions were assayed for polymerization activity using [32P]RNA representing the psbA gene and GTP. Equivalent results were obtained when ATP, GTP, or ADP was used. Following incubation, the RNA was analyzed using denaturing gel electrophoresis (upper panel). The presence of PNPase in each fraction was analyzed using immunoblotting (lower panel). The migration of molecular weight markers thyroglobulin (669 kDa), RubP-carboxylase (550 kDa), and catalase (232 kDa) fractionated on the same column is shown at the top of the left panel. Only the column fractions having molecular masses exceeding 232 kDa are shown, since no activity whatsoever was detected in any other fraction. (B) The three fractions of the Superdex 200 column containing polymerization activity, as shown at the bottom of panel A, were pooled and loaded on a heparin column. The unbound (FT) and bound (B) fractions were analyzed as described in the legend to panel A for the Superdex 200 column. (C) The bound fraction of the heparin column was dialyzed and applied to a Mono-Q column that was developed with a KCl gradient. Fractions 26 to 32 were found to possess all of the polymerization activity and the PNPase polypeptide (see Fig. 3).