Figure 4.
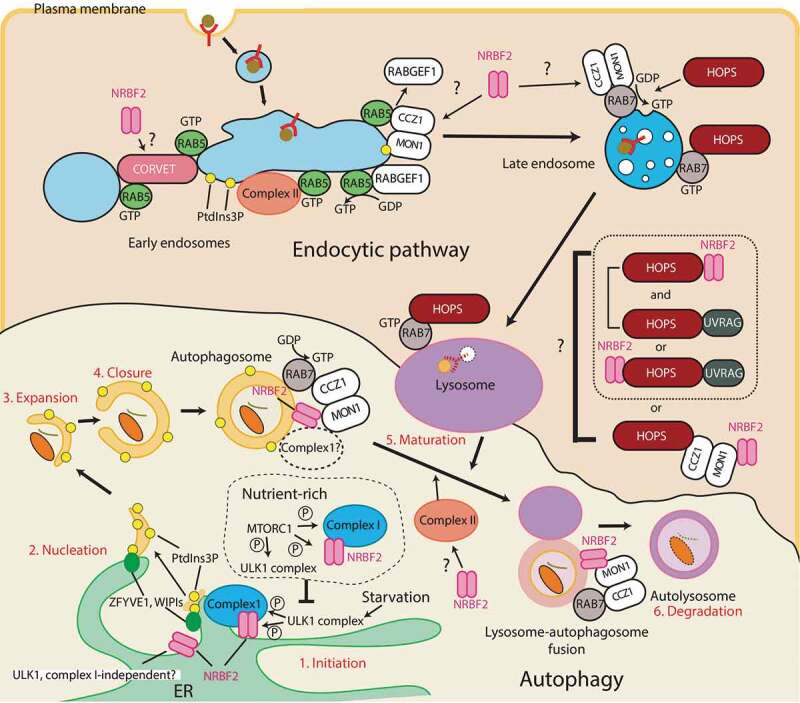
Autophagy and endocytic pathways that involve NRBF2. Autophagy: In nutrient-rich conditions, MTORC1 inhibits autophagy by phosphorylating the ULK1 complex and complex I-NRBF2 complex. Upon starvation, MTORC1 is inactivated, leading to the ULK1 complex activation that recruits complex I-NRBF2, which in turn produces PtdIns3P (1. Inititation). PtdIns3P recruits its effectors such as DFCPs and WIPIs at omegasomes that causes nucleation of phagophores (2. Nucleation). The phagophore expands (3. Expansion), then closes (4. Closure) to become an autophagosome. The autophagosome fuses with lysosomes to become an autolysosome (5. Maturation). The cargos are eventually degraded in the autolysosome (6. Degradation). As well as the initiation step, NRBF2 is also involved in the autophagy maturation step by associating with the MON1-CCZ1 complex. The NRBF2-MON1-CCZ1 facilitates the GEF activity of RAB7, which is involved in the maturation step. Circled P: phosphorylation; ?: the direct involvement of NRBF2 has not been confirmed. Endocytic pathway: During endocytosis, lipids and surface proteins including ligand-receptor complexes are internalized. The endocytosed vesicle first fuses with the early endosome marked by RAB5. The early endosome matures into the late endosome marked by RAB7, then the late endosome eventually fuses with lysosomes to degrade the endocytosed cargos. The early to late endosome transition is mediated by the MON1-CCZ1 complex. The CORVET and HOPS complexes facilitate the tethering of early endosomes and late endosomes, respectively. NRBF2 was found to interact with VPP33A, the common subunit between the CORVET and HOPS complexes. Also, NRBF2 is known to interact with the MON1-CCZ1 complex during autophagy and phagocytosis, but it remains to be seen whether this interaction also occurs in the endocytic pathway or not. The complex II-specific UVRAG subunit is also known to bind to the HOPS complex independently of complex II. It has been unclear whether the NRBF2 and UVRAG interactions with the HOPS complex are mutually exclusive or not
