Figure 1.
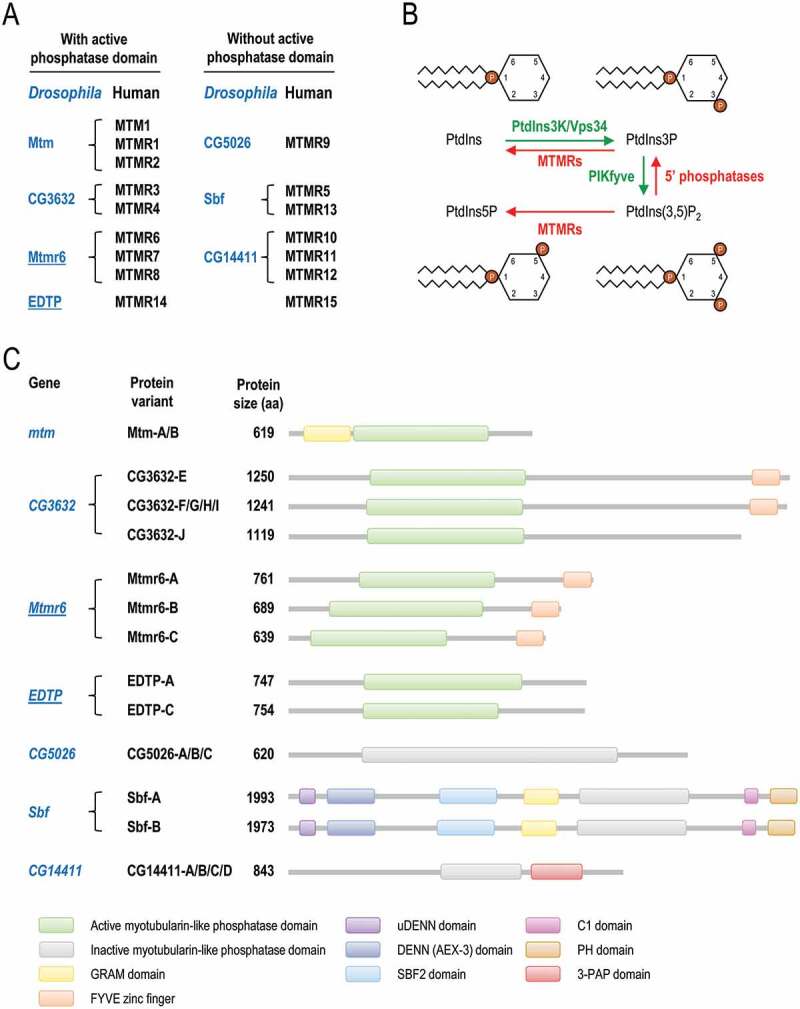
Classification and molecular functions of MTMRs in flies and mammals. (A) Human myotubularin (MTM) and myotubularin-related (MTMR) phosphatases (black) and their fly orthologs (blue). Proteins were grouped according to the presence or absence of active phosphatase domain. EDTP and Mtmr6, the two Drosophila paralogs that were analyzed in this study, are underlined. (B) MTMRs dephosphorylate PtdIns3P to PtdIns, thereby antagonizing the class III PtdIns3K. MTMRs also convert PtdIns(3,5)P2 to PtdIns5P. PtdIns3P, PtdIns5P and PtdIns(3,5)P2 are each involved in autophagy. (C) Scaled representation of the protein domains of Drosophila myotubularins based on Pfam predictions. Abbreviations: 3-PAP: 3-phosphatase adapter protein; C1: phorbol esters/diacylglycerol binding; DENN: differentially expressed in neoplastic versus normal cells; FYVE: Fab1 (yeast ortholog of PIKfyve), YOTB, Vac1 (vesicle transport protein) and EEA1; GRAM: glucosyltransferases, Rab-like GTPase activators and myotubularins; PH: pleckstrin homology; Sbf: SET domain binding factor
