Figure 2.
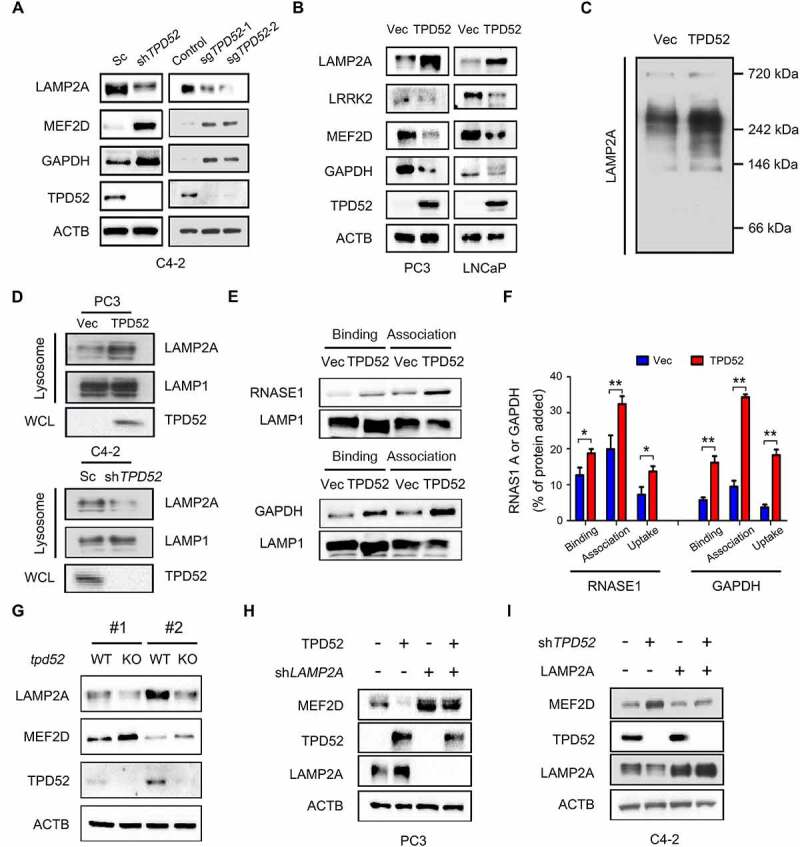
Identification of TPD52 as an activator of CMA. (A) IB analysis of the whole-cell lysates (WCLs) derived from TPD52-knockdown C4-2 cells generated using shRNA and TPD52-knockout C4-2 cells generated using sgRNA. (B) IB analysis of the WCLs derived from TPD52-overexpressing PC3 and LNCaP cells. (C) Native continuous gel electrophoresis and IB analysis of the lysosomes purified from PC3 cells transfected with vector (Vec) or TPD52. (D) IB analysis of the WCLs and lysosomal LAMP2A purified from TPD52-overexpressing PC3 cells and TPD52-knockdown C4-2 cells. (E–F) Binding, association and uptake of proteins by the lysosomes were calculated from the quantification of the CMA substrates RNASE A and GAPDH, based on the IB analysis of the lysosomes from TPD52-overexpressing PC3 cells that were either untreated or pretreated with protease inhibitors (PI). Representative immunoblots (E) and the densitometric quantification of two or three immunoblots from different experiments (F) are shown. Error bars represent SE. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. (G) IB analysis of the WCLs derived from wild-type (WT) or tpd52-knockout (KO) mouse prostate tissues. (H) IB analysis of the WCLs derived from TPD52-overexpressing PC3 cells transfected with or without LAMP2A shRNA (shLAMP2A). (I) IB analysis of the WCLs derived from TPD52-knockdown C4-2 cells transfected with or without the LAMP2A plasmid
