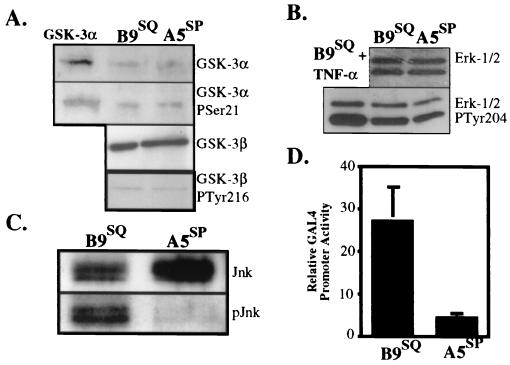
FIG. 6.
B9SQ cells possess significantly more active JNK than do A5SP cells. (A) Immunoblots for total GSK-3α (top panel) and its inactive Ser 21 phosphoform (second panel from top) and for total GSK-3β (third panel from top) and its active Tyr 216 phosphoform (bottom panel) in 5 μg of whole-cell extracts from B9SQ and A5SP cells. (B) Immunoblots for ERK-1 and ERK-2 (top panel) and their active forms (bottom panel). Nuclear extracts (20 μg) from B9SQ cells stimulated with tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) were used as a positive control for the ERK active forms. (C) Immunoprecipitation-immunoblot for JNK protein using 10 μl of anti-JNK beads and 500 μl of total cell extracts. Immunoblotting was performed using antibodies recognizing total (Jnk) or active (phosphorylated at Thr 183 and Tyr 185) (pJnk) JNK. (D) In vivo assay for JNK activity in B9SQ and A5SP cells. B9SQ and A5SP cells were transiently transfected with a GAL4 UAS reporter construct and an expression construct encoding either a fusion protein containing the amino-terminal transactivation domain (JNK substrate) of c-Jun fused to GAL4dbd or GAL4dbd alone. Luciferase activity was measured and is shown as the activity of the c-Jun–GAL4dbd fusion normalized to that of GAL4dbd alone (n = 4) for each cell line.