Fig. 6. Impact of checkpoint inhibitor treatment on anti-MM activities of XBP1/CD138/CS1-specific CTL.
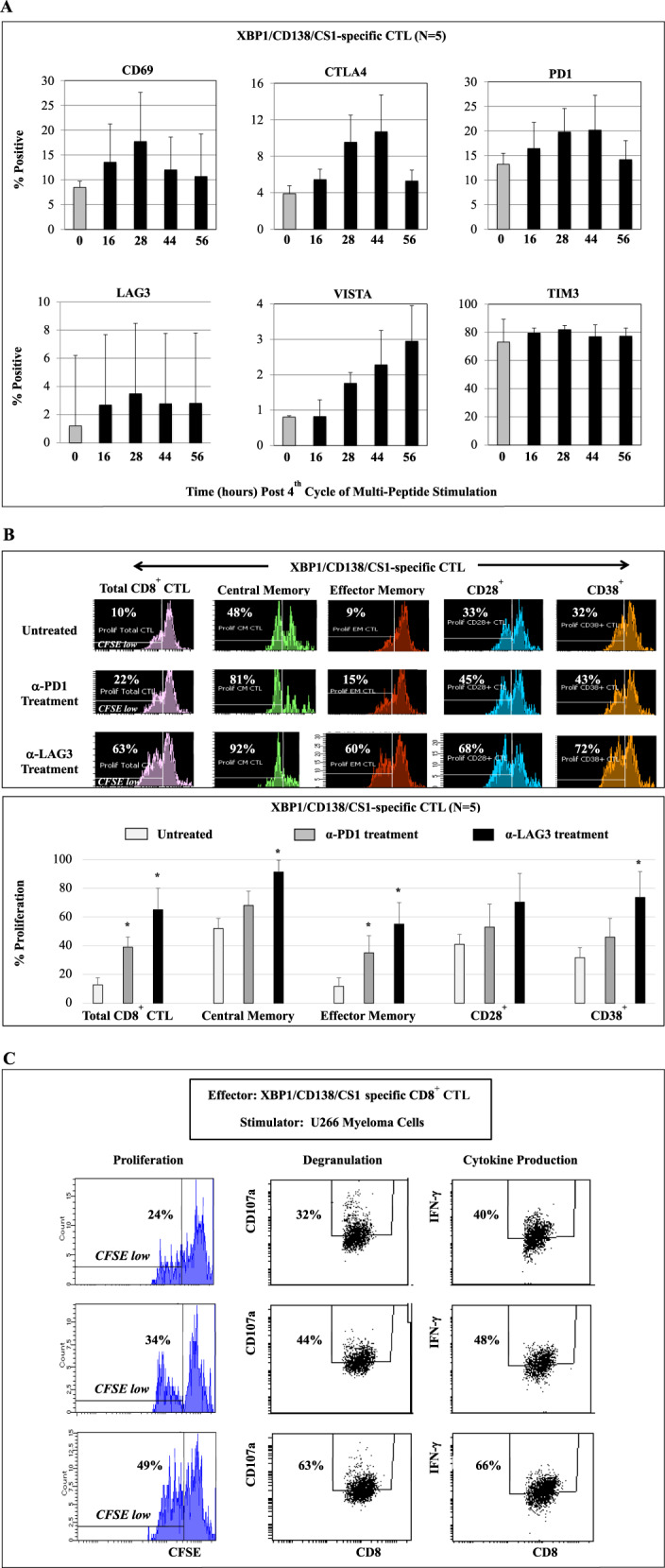
HLA-A2-specific XBP1/CD138/CS1-specific CTL (N = 5) were generated by four cycles of weekly stimulation of CD3+ T cells with immunogenic XBP1/CD138/CS1 peptides and then examined for their phenotypic profile and functional activities against MM. A Upon fourth cycle of peptides stimulation, time-dependent T-cell activation (CD69) and checkpoint (CTLA4, PD1, LAG3, VISTA, TIM3) upregulation were detected on MM-specific CTL. B, C Immune checkpoint treatment enhanced (anti-LAG3 > anti-PD1) the poly-functional activities of antigen-specific T cells in response to HLA-A2-matched U266 MM cells. B Induced proliferation of total CD8+ CTL as well as central memory, effector memory, CD28+ and CD38+ CTL subsets. C Increased CD107a+ degranulation and IFN-γ production associated with a higher CD8+ CTL proliferation.
