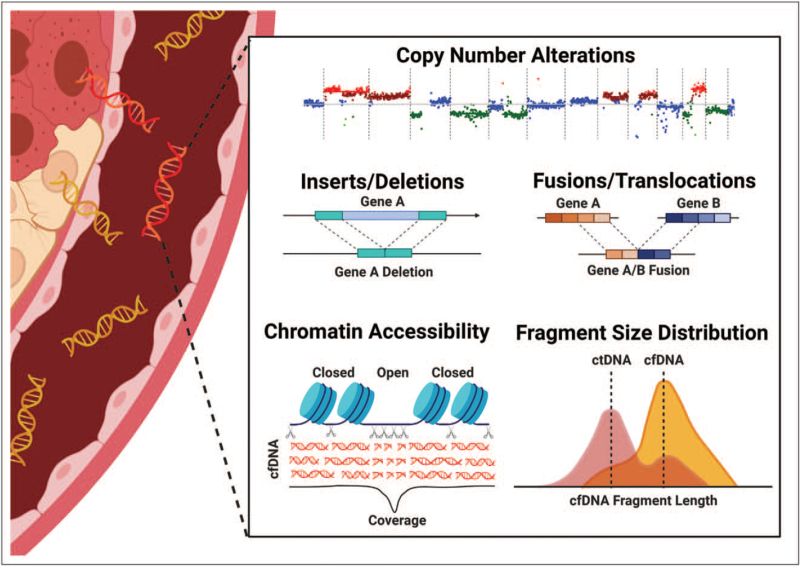
FIGURE 2.
Moderate depth whole genome sequencing improve detection by enabling multiomic integration from a single assay. Recent studies have demonstrated that, with advanced bioinformatic analysis, WGS to depths of 12x–35x is sufficient for detection of copy number alterations, indels, translocations and fusions, assessment of chromatin accessibility and fragmentomics [51▪▪,97▪▪]. In addition to detecting the most common genomic alterations in childhood cancer, therefore, integration of these output also infers epigenetic and transcriptomic signatures. Combinatorial approaches, previously requiring multiple assays, enhance detection of early stage cancers.