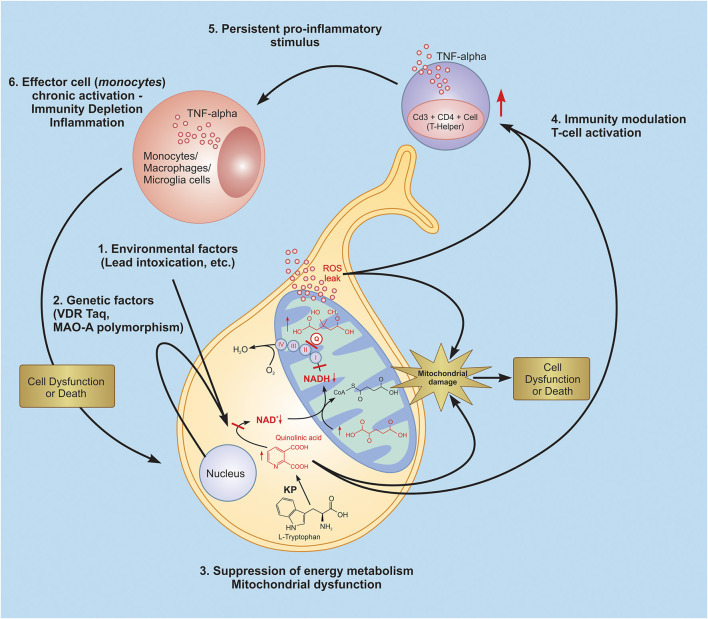
Figure 12.
Probable glance at inflammatory scenario development in autistic pathology. Lead intoxication, the effect of which is intensified by a mutation of the VDR-Taq and MAO-A leads to quinolinic acid increase, resulting in energy metabolism depletion and mitochondrial dysfunction, which is expressed in ROS overproduction. The latter are also known to be signal-trigger molecules which activate the T-cell dependent immune response. Activated T-helpers produce pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α), which leads to the activation of effector cells - macrophages and the development of a chronic inflammatory response and induce persistent inflammatory signals. KP, kynurenine pathway; Q, coenzyme Q10.