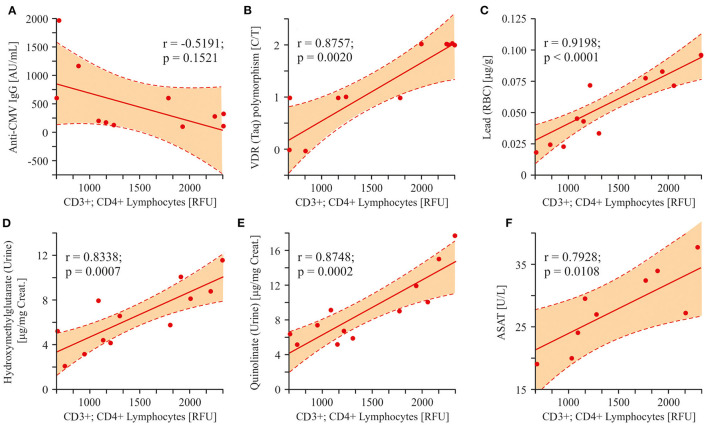
Figure 9.
Linear regression analysis (Pearson product-moment correlation) of the interrelation between CD3+CD4+ lymphocytes and some ASD etiological factors and markers associated with mitochondrial damage. (A–C) The interrelation between T-helper cells and some probable ASD etiological factors (Cytomegalovirus infection, VDR(Taq) SNP polymorphism, Lead content in packed RBC). VDR(Taq) SNP and the Lead content in packed RBC highly correlated with helper T-cells (r = 0.8757; p = 0.0020 and r = 0.9198; p < 0.0001, respectively). (D–F) The interrelation between T-helper cells and some analytes associated with mitochondria damage (HMG, QUIN, ASAT). A strong correlation was found between HMG, QUIN, ASAT and the content of T-helper lymphocytes (r = 0.8338; p = 0.0007, r = 0.8748; p = 0.0002, r = 0.7928; p = 0.0108). Pearson correlation coefficients were computed to determine inter-metabolite correlations. P < 0.05 were used to indicate statistical significance.