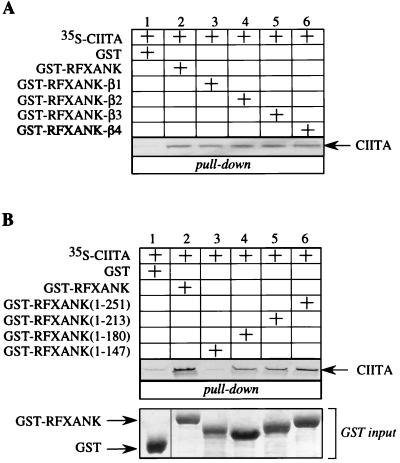
FIG. 5.
The ankyrin repeat domain of RFXANK also binds to CIITA. (A) β-Hairpin loops of RFXANK ankyrin repeats are not involved in binding to CIITA. The mutant GST-RFXANK-β1 to −4 fusion proteins were used in a GST pull-down assay. 35S-labeled CIITA was incubated with GST alone or with the wild-type and mutant GST-RFXANK fusion proteins and selected on glutathione-Sepharose beads. Retained CIITA is depicted with an arrow. Lanes 1 to 6, results of the binding assay. Pluses above the autoradiographs indicate the presence of different proteins in the assay. Amounts of GST alone together with the wild-type and mutant GST-RFXANK fusion proteins were the same as in Fig. 3 (GST input) and are therefore not presented; 10% input 35S-labeled CIITA was the same as in Fig. 4A, lane 3. (B) Ankyrin repeats as structural units are required for CIITA binding. The first 251, 213, 180, and 147 amino acid residues of RFXANK represent the mutant RFXANK proteins that retain four, three, two, and one (the first) ankyrin repeat(s), respectively, and are fused to GST. All four C-terminal deletion mutants of GST-RFXANK were used in a GST pull-down assay similar to that described for panel A. Lanes 1 to 6, results of the binding assay. The amounts of all of the GST fusion proteins were the same and are shown in the Coomassie blue-stained gel at the bottom of the panel (GST input).