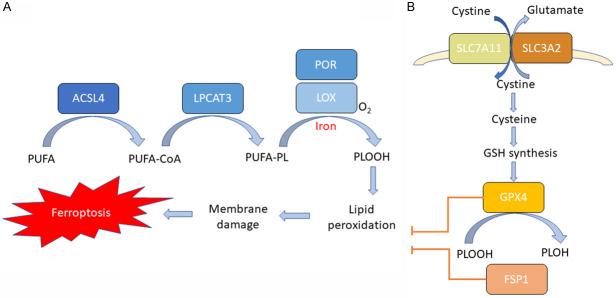
Figure 1.
Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis. A. Lipid peroxidation pathways. ACSL4 catalyzes the ligation of long-chain PUFAs with CoA, and LPCAT3 promotes the esterification and incorporation of these products into membrane phospholipids (PL). PUFA-containing PL is oxidized by iron-dependent enzymes LOX or POR, resulting in lipid peroxidation, membrane damage and subsequent ferroptosis. B. Antioxidant pathways. Cysteine is imported into the cell by SLC7A11/SLC3A2 complex for the synthesis of GSH. GPX4 uses GSH as a substrate and reduces the membrane phospholipid hydroperoxide to harmless lipid alcohols, thereby preventing the accumulation of lethal lipid ROS and suppressing ferroptosis. Alternatively, cells utilize FSP1 axis to suppress lipid peroxidation and prevent ferroptosis.