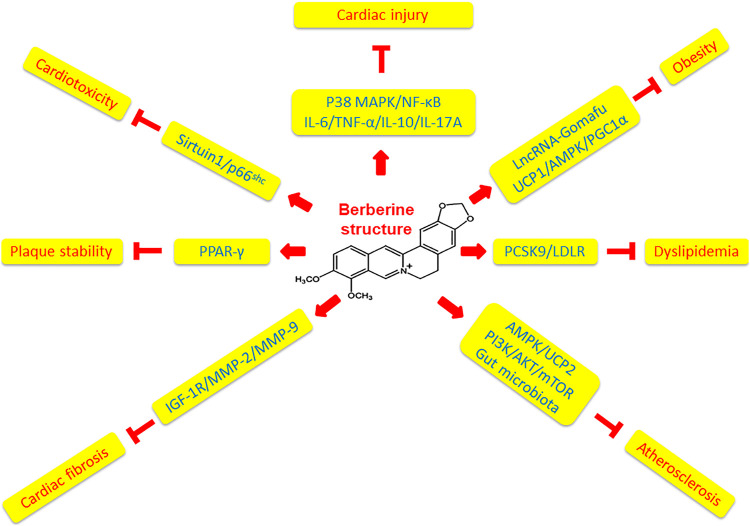
FIGURE 2.
Mechanisms of berberine affecting atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases. Berberine has pleiotropic effects on cardiovascular diseases via multiple mechanisms. Berberine protects cardiac injury by downregulating the expression of inflammatory cytokines including IL-6, TNF-α, IL-10 and IL-17A via p38 MAPK-mediated NF-κB signaling pathways. Berberine ameliorates obesity via downregulating lncRNA Gomafu and modulating UCP1/AMPK/PGC1α signaling pathways. Berberine inhibits dyslipidemia through regulating PCSK9/LDLR pathways. Berberine suppresses atherosclerosis via activating AMPK/UCP2 signaling pathways, regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR molecular pathways, and modulating gut microbiota. Berberine reduces cardiac fibrosis via inhibiting IGF-1R/MMP-2/MMP-9 signaling pathways. Berberine activates PPARγ to increase atherosclerotic plaque stability. Berberine ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through Sirtuin1/p66shc pathways.