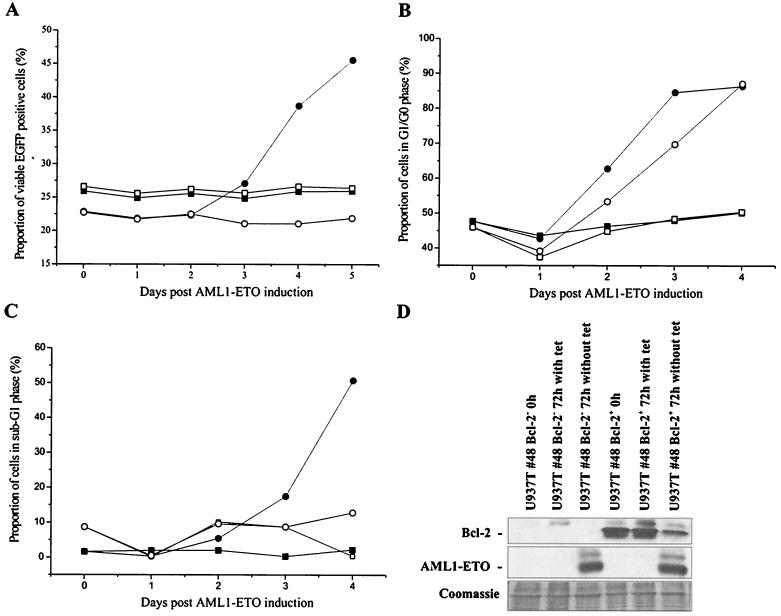
FIG. 6.
Ectopic expression of Bcl-2 delays apoptosis in U937T-A/E cells. (A) U937T-A/E cells were infected with either MSCV–Bcl-2–IRES–EGFP (circle) or MSCV-IRES-EGFP (square) and cultured in the presence (open symbol) or the absence (closed symbol) of tetracycline (1 μg/ml). Retrovirus-infected cells were confirmed based on EGFP fluorescence. Apoptotic and necrotic cells were discriminated from viable cells by double annexin V-PE and 7-AAD staining. (B and C) Cell cycle analysis of U937T-A/E pool 48 cells infected with MSCV–Bcl-2–IRES–EGFP upon tetracycline withdrawal. The cell cycle distribution was determined by propidium iodide staining of the cell nuclei at different time points as indicated. The cells were initially sorted on the basis of EGFP expression. Open symbols, EGFP+ cells; solid symbols, EGFP− cells. The cells were cultured in the presence (square) or absence (circle) of tetracycline and were analyzed by flow cytometry. (B) Cells in G0/G1 phase; the percentage does not reflect the proportion of cells in sub-G1 phase. (C) Proportion of cells in sub-G1 phase (apoptotic) compared to the total population. (D) Western blot analyses showing the expression of Bcl-2 and AML1-ETO proteins in EGFP+ and EGFP− U937T-A/E pool 48 cells infected with MSCV–Bcl-2–IRES–EGFP following tetracycline withdrawal for 72 h. Coomassie staining is shown to indicate the relative amount of protein in each lane.