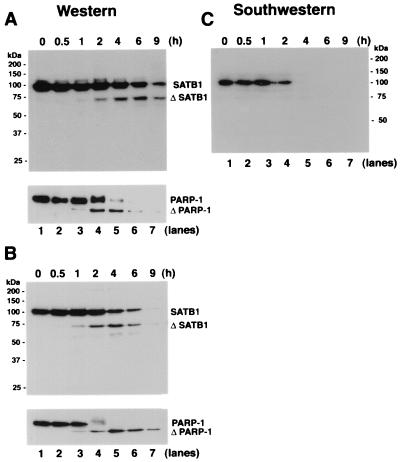
FIG. 2.
Proteolytic cleavage of SATB1 early during T-cell apoptosis. (A) Cleavage of SATB1 in mouse thymocytes. Thymocytes were collected from a 3-week-old mouse, treated with 2 μM dexamethasone to induce apoptosis, and harvested. Nuclear extracts were prepared as described in Materials and Methods, and 20 μg of protein was resolved by SDS–10% PAGE, transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane, and probed with anti-SATB1. Left, positions of the molecular weight markers; right, positions of the intact and cleaved (Δ) SATB1. Bottom, immunoblot analysis of the same extracts using anti-PARP-1. Positions of intact and cleaved (Δ) PARP-1 are indicated. (B) Cleavage of SATB1 in a human lymphoblastic T-cell line. Jurkat cells were grown continuously for 8 days in culture as described in Materials and Methods and treated with 100 ng of anti-Fas antibody (clone CH-11)/ml to induce apoptosis. Cells were harvested at the indicated times (0.5 to 9 h) thereafter. Nuclear extracts were prepared, and 20 μg of protein was resolved by SDS–10% PAGE and analyzed for SATB1 by Western blotting. Bottom, status of PARP-1 in identical extracts. (C) Loss of BUR-binding activity during apoptosis. The same series of proteins used in panel A were separated on a 10% polyacrylamide gel except that the gel was run longer than for panel A and subjected to Southwestern analysis as described in Materials and Methods using a radiolabeled WT (25)7-mer probe. The autoradiogram shows a signal corresponding to the BUR-binding activity of intact SATB1. The various time points after dexamethasone treatment (in hours) are indicated above each lane.