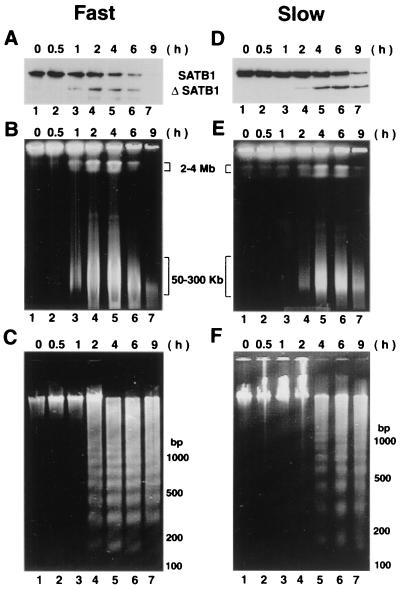
FIG. 3.
High-molecular-weight DNA fragmentation coincides with SATB1 cleavage. (A and D) Immunoblot analysis of SATB1 in apoptotic Jurkat cells. Jurkat cells were treated with anti-Fas, and the fate of SATB1 was monitored by immunoblot analysis of cell extracts as described in Materials and Methods. (B and E) Cleavage of genomic DNA into 50- to 300-kb chromatin loops. Pulsed-field gel electrophoretic separation of apoptotic Jurkat cell DNA was performed as described in Materials and Methods. Jurkat cells were induced for apoptosis using anti-Fas antibody (clone CH-11). At defined time points (0.5 to 9 h) postinduction aliquots of cells were removed and embedded in LMP agarose. The agarose plugs were lysed and deproteinized as described in Materials and Methods. The digested plugs were then loaded onto a 1% agarose gel, and the high-molecular-weight DNA was resolved by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis as described in Materials and Methods. Positions of the 50- to 300-kb chromatin loops and 2- to 4-Mb giant DNA fragments are indicated. (C and F) Low-molecular-weight DNA fragmentation. Low-molecular weight DNA was prepared from apoptotic Jurkat cells as described previously (55). For all panels, time (in hours) after the anti-Fas treatment of cells in culture is indicated on top. Two different seeding densities were used to culture Jurkat cells as described in Materials and Methods. Fast (A to C), apoptotic cleavage profiles from an 8-day continuous culture seeded at 5 × 104 cells/ml; slow (D to F), apoptotic cleavage profiles from a 2-day culture seeded at 2 × 105 cells/ml.