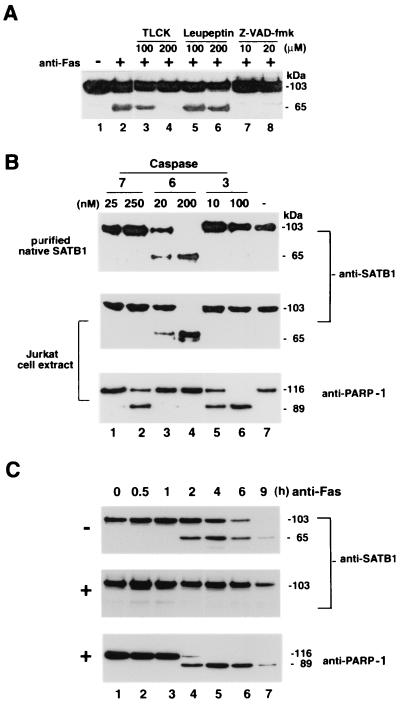
FIG. 4.
Identification of protease that cleaves SATB1 during apoptosis. (A) Effect of protease inhibitors on in vivo SATB1 cleavage in Jurkat cells treated with anti-Fas antibody. Jurkat cells were preincubated with control solvent (−) or with specific protease inhibitors for 30 min as indicated. An anti-CD95 monoclonal antibody (clone CH-11) was then added (+) to a final concentration of 100 ng/ml, the cells were incubated further for 3 h, and SATB1 proteolysis was analyzed by immunoblotting. The 65-kDa band represents the major proteolytic degradation product of SATB1. (B) In vitro cleavage by purified caspases 7, 6, and 3. Purified native SATB1 from mouse thymus (top) and Jurkat whole-cell extract (middle and bottom) were incubated with indicated amounts of caspase 7 (lanes 1 and 2), 6 (lanes 3 and 4), or caspase 3 (lanes 5 and 6) or without caspase (lane 7) for 1 h and examined for SATB1 (top and middle) and PARP-1 (bottom) cleavage by Western blotting using the appropriate antibody. (C) In vivo inhibition of SATB1 cleavage by a caspase 6 inhibitor. Jurkat cells were preincubated with solvent dimethyl sulfoxide alone (−; top) or with 10 μM Z-VEID-fmk (+; middle and bottom) for 30 min. Anti-Fas antibody was then added to a final concentration of 100 ng/ml. Aliquots of cells were removed at indicated times, and protein extracts were prepared as described in Materials and Methods. SATB1 proteolysis was analyzed by immunoblotting as described in Materials and Methods. As a marker for apoptosis, the Western blot (middle) was stripped and reprobed (bottom) with anti-PARP-1 (H-250).