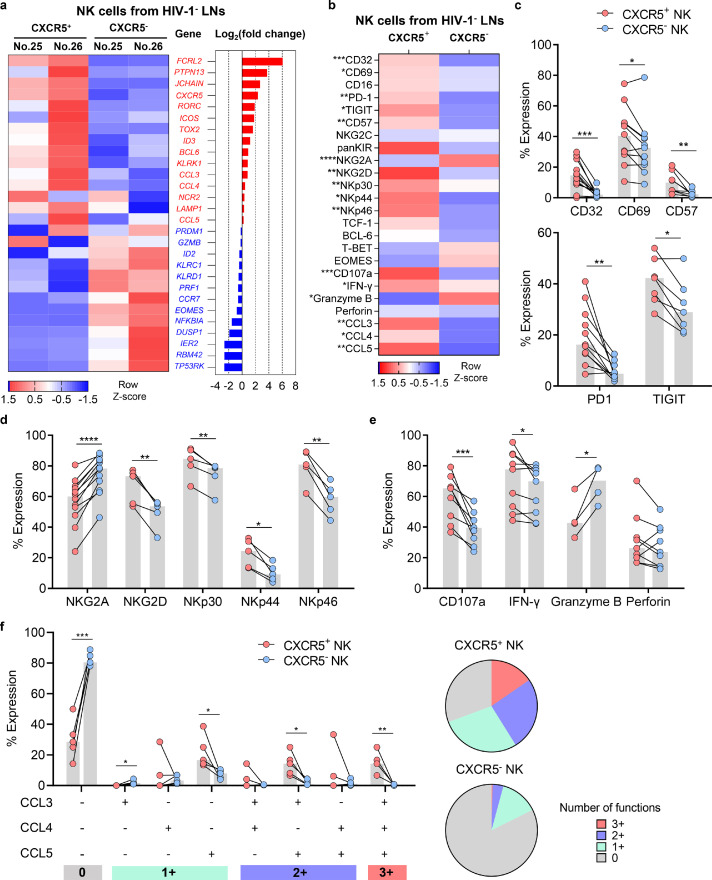
Figure 2.
Phenotypic and functional profiles of CXCR5+ and CXCR5− NK cells in HIV-1 negative LNs. (a) RNA-seq were performed to investigate the relative expression of indicated genes in CXCR5+ and CXCR5− NK cells from two HIV-1− LNs. (b) Flow cytometry were performed to investigate the protein expression phenotypes of CXCR5+ and CXCR5− NK cells from HIV-1− LNs. (c) The expression of CD69 (n = 11), CD32 (n = 12), CD57 (n = 8), PD-1 (n = 11) and TIGIT (n = 7) on CXCR5+ and CXCR5− NK cells from HIV-1− LNs. (d) The expression of NK surface receptors (NKG2A, n = 12; NKG2D, n = 5; NKp30, n = 5; NKp44, n = 5; NKp46, n = 5) on CXCR5+ and CXCR5− NK cells from HIV-1− LNs. (e-f) The expression of (e) CD107a (n = 9), IFN-γ (n = 9), granzyme B (n = 4), perforin (n = 9) and (f) β-chemokines (CCL3, CCL4 and CCL5, n = 5) in CXCR5+ and CXCR5− NK cells which were stimulated with IL-12 (10 ng/ml), IL-15 (20 ng/ml) and IL-18 (100 ng/ml) for 16 h. Significant differences in b, c, d, e, and f were calculated using Wilcoxon signed-rank test. *P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.