FIGURE 7.
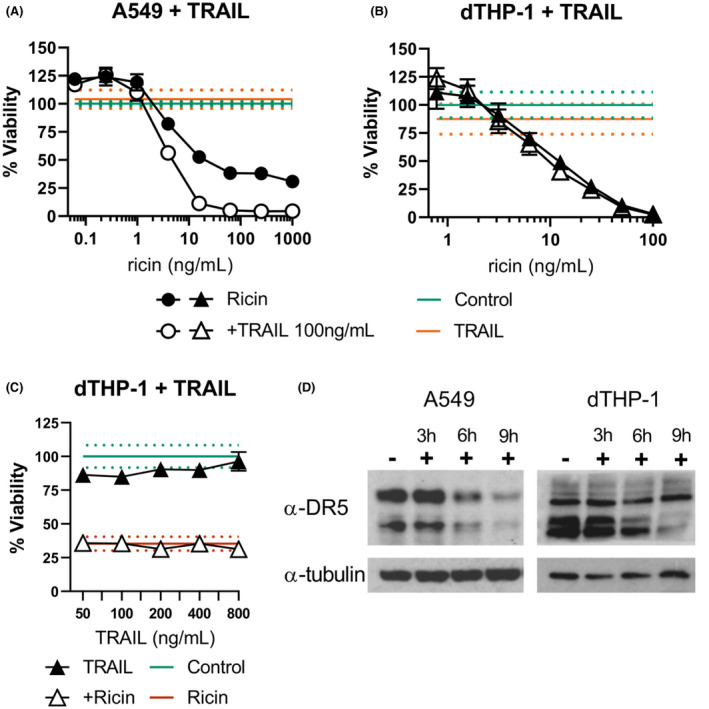
Impact of TRAIL on A549 and dTHP‐1 sensitivities to ricin. (A) Ricin +TRAIL co‐treatment sensitizes A549 cells to ricin‐induced cell death (AUC of 5278 ±321 vs. 36,190 ±4027 for ricin‐only treated), but (B) TRAIL has no effect on ricin cytotoxicity in dTHP‐1 cells (AUC of 1924 ±223 vs. 2161 ±167 for ricin‐only treated). (C) TRAIL co‐treatment failed to influence ricin‐induced dTHP‐1 cell death even at much higher doses (12.5 ng/ml ricin). (D) Western blots analysis of A549 and dTHP‐1 cells demonstrate DR5/TRAILR2 expression in both cell types, the primary death receptor for TRAIL (Cell Signaling Technology Cat# 8074, RRID:AB_10950817). α‐tubulin served as the loading control (Cell Signaling Technology Cat# 5346, RRID:AB_1950376). Closed symbols, ricin‐only; open symbols, dual treatment, error bars represent the 95% CI. Green lines and dots and red lines and dots represent the mean and 95% CI of control‐ and ricin‐treated cells, respectively. Orange lines and dots represent the independent effect of TRAIL. Data presented are the mean of eight replicate wells with the 95% confidence interval. Graphical representation of the unnormalized data and results of pairwise statistical testing for treatment interactions are available in Figure S10. Refer to Figure S11 to observe the original films from which DR5 blot images were derived
