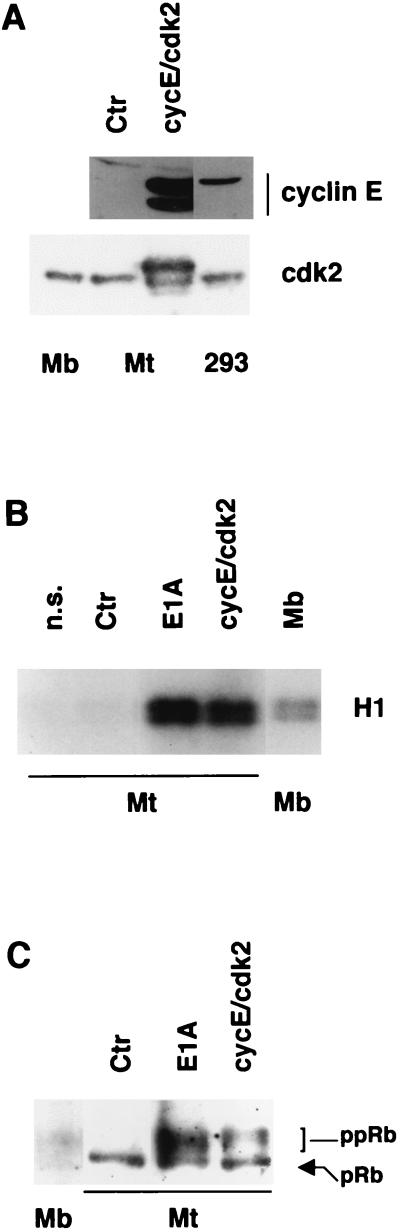
FIG. 1.
Exogenous cyclin E and cdk2 expression. (A) Western blot analysis of C2C12 myotubes (Mt) infected with the Ad-Track control virus (Ctr; MOI, 300) or with the Ad-cycE and Ad-cdk2 viruses (cycE/cdk2; MOIs, 200 and 350, respectively) at 48 h p.i. Proliferating C2C12 myoblasts (Mb) and/or human 293 cells, expressing high levels of endogenous cyclin E, are shown for comparison. 293 cells are shown because human cyclin E levels in myotubes could not be compared with those physiologically expressed in mouse C2C12 myoblasts, since an antibody reacting equally with murine and human cyclin E was not available. (B) Cyclin E-associated kinase activity immunoprecipitated from myotubes infected with Ad-cycE and Ad-cdk2, the E1A-expressing virus dl520 (for reference), or a control virus. Myoblasts are shown for comparison. A nonspecific (n.s.) antibody was used as a control. The precipitates were assayed by using histone H1 (H1) as the substrate. (C) Western blot analysis of pRb in myotubes infected with the Ad-cycE and Ad-cdk2, dl520, and control viruses and myoblasts. The slow-migrating, hyperphosphorylated (ppRb) and the hypophosphorylated (pRb) forms of Rb are indicated.