Figure EV1. High salt is an instant promotion factor of viral infection.
-
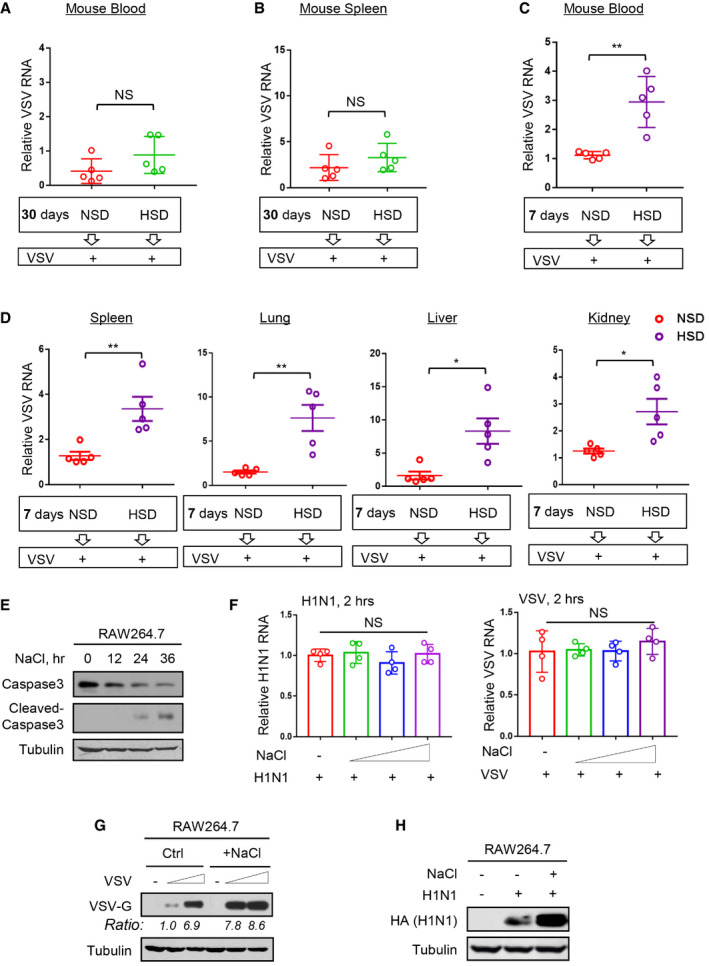
A, BMice (n = 5) were fed an NSD (0.45% NaCl) or HSD (4% NaCl) for 30 days and then intraperitoneally infected with VSV (1 × 108 PFU per gram body, 48 h). VSV RNA levels in mouse blood (A) or spleen (B) were detected by RT‐qPCR.
-
C, DMice (n = 5) were fed an NSD (0.45% NaCl) or HSD (4% NaCl) for 7 days and then intraperitoneally infected with VSV (1 × 108 PFU per gram body, 48 h). VSV RNA levels in mouse blood (C) or different tissues (spleen, lung, liver, and kidney) (D) were detected by RT‐qPCR.
-
EWestern blot analysis of Caspase 3 and cleaved‐Caspase 3 in RAW264.7 cells treated with additional NaCl (+51 mM) for 12, 24, and 36 h.
-
FRT–qPCR analysis of viral RNA levels in RAW264.7 cells infected with H1N1 or VSV (MOI = 1.0) for only 2 h immediately after addition of NaCl (+17, 34, and 51 mM).
-
GRAW264.7 cells were infected with VSV (MOI = 1.0 and 2.0, 24 h) immediately after addition of NaCl (+34 mM). VSV‐G protein levels were analyzed by western blot.
-
HRAW264.7 cells were infected with H1N1 (MOI = 1.0, 24 h) immediately after addition of NaCl (+34 mM). H1N1‐encoded HA protein levels were analyzed by western blot.
Data information: Data (A–D) show mean and SEM of five biological replicates; Data (E, G, H) are representative of at least two biological replicates; Data (F) represent mean and SD of four biological replicates. For all statistical testing: P‐values were calculated using two‐tailed unpaired Student’s t‐test. N.S, not significant (P > 0.05). *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.
Source data are available online for this figure.
