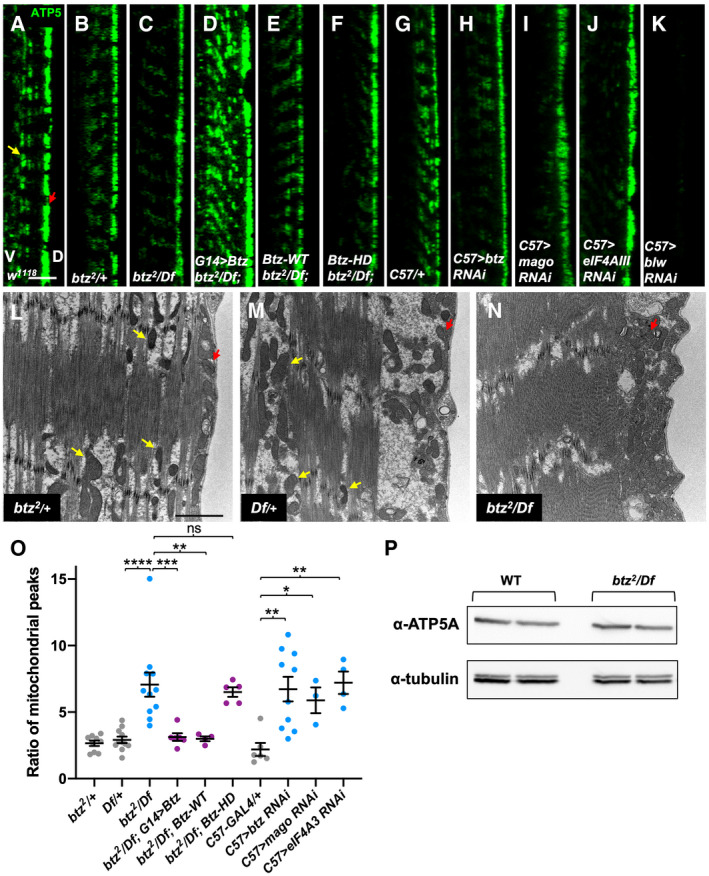
Figure 2. Btz acts as an EJC component to control the distribution of mitochondria in muscle.
-
A–KConfocal xz‐sections of larval muscle 6 in segment A3 stained with anti‐ATP5A to label mitochondria. The dorsal surface (D) is to the right and ventral (V) to the left. (A) white (w)1118 control; (B) btz2 /+ heterozygote; (C) btz2 / Df(3R)BSC497; (D) G14‐GAL4/UAS‐btz; btz2 / Df(3R)BSC497; (E) Btz‐WT; btz2 / Df(3R)BSC497; (F) Btz‐HD; btz2 / Df(3R)BSC497; (G) C57‐GAL4/+ control; (H) C57‐GAL4>UAS‐btz RNAi; (I) C57‐GAL4>UAS‐mago RNAi; (J) C57‐GAL4>UAS‐eIF4AIII RNAi; (K) C57‐GAL4>UAS‐blw RNAi. In wild‐type muscles, mitochondria are present at the dorsal surface (red arrow in A) and also distributed between the fibers (yellow arrow in A), while in btz mutant muscles and in muscles expressing btz, mago, or eIF4AIII RNAi, they are concentrated at the dorsal surface. Expression of UAS‐btz in muscle or the presence of the wild‐type, but not the HD mutant, Btz transgene restores the wild‐type distribution to btz mutants. The loss of ATP5A staining in muscles in which blw is knocked down confirms that the signal is specific. Scale bars, 10 μm.
-
L–NElectron micrographs showing cross‐sections of larval muscle 6 in segment A3, with the dorsal surface to the right. (L) btz2 /+; (M) Df(3R)BSC497/+; (N) btz2 / Df(3R)BSC497. Yellow arrows indicate examples of mitochondria interspersed between muscle fibers, and red arrows indicate mitochondria at the dorsal surface. Scale bars, 2 μm.
-
OQuantification of the ratio of the dorsal surface peak of ATP5 intensity to the second highest peak for the genotypes indicated. ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05; ns, not significant by Mann–Whitney test. n = 9 (btz/+), n = 11 (Df/+, btz/Df), n = 6 (btz/Df; G14>btz, C57‐GAL4/+), n = 4 (btz/Df; Btz‐WT, C57>eIF4AIII RNAi), n = 5 (btz/Df; Btz‐HD), n = 10 (C57>btz RNAi), or n = 3 (C57>mago RNAi). Error bars show mean ± SEM.
-
PWestern blot of wild type (Canton S) and btz2 /Df(3R)BSC497 larval carcasses with anti‐ATP5A and anti‐tubulin. Duplicate samples of 15 ng total protein are shown for each genotype. The overall level of ATP5A is not altered in btz mutant muscles.
Source data are available online for this figure.
