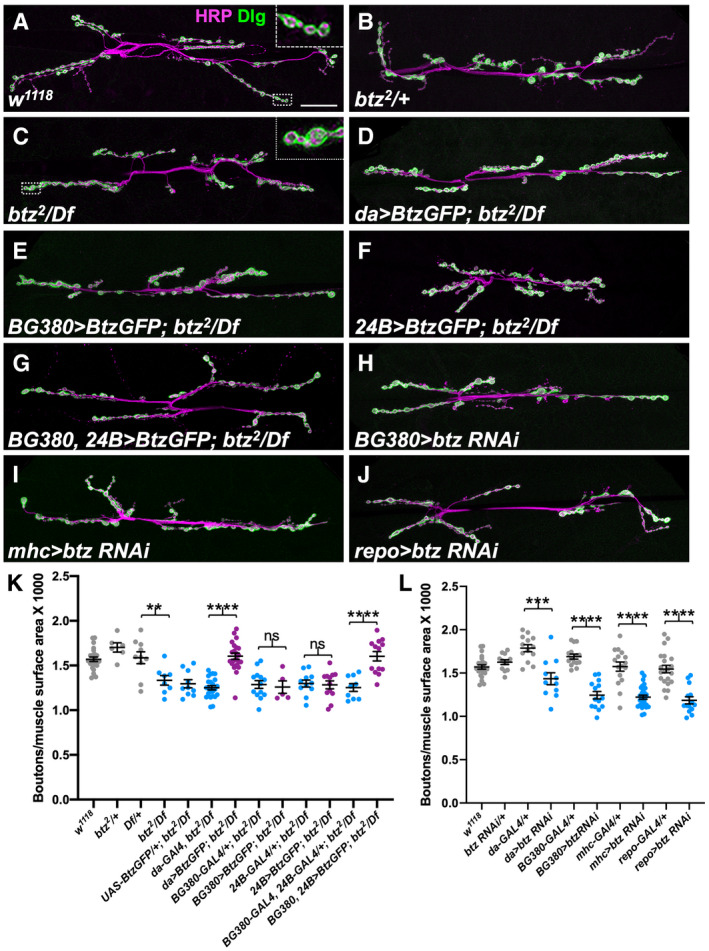
Figure 3. Btz acts in muscles, motor neurons, and glia to control NMJ size.
-
A–JConfocal images of the NMJ on larval muscles 6 and 7 in segment A3, stained with anti‐HRP (magenta) to label the nerve and anti‐Dlg (green) as a postsynaptic marker of synaptic boutons. (A) w1118 control; (B) btz2 /+; (C) btz2 /Df(3R)BSC497; (D) UAS‐btz/+; da‐GAL4, btz2 /Df(3R)BSC497; (E) BG380‐GAL4/+; UAS‐btz/+; btz2 /Df(3R)BSC497; (F) 24B‐GAL4/UAS‐btz; btz2 /Df(3R)BSC497; (G) BG380‐GAL4/+; 24B‐GAL4/UAS‐btz; btz2 /Df(3R)BSC497; (H) BG380‐GAL4/+; UAS‐btz RNAi/+; (I) mhc‐GAL4/UAS‐btz RNAi; (J) repo‐GAL4/UAS‐btz RNAi. Scale bar, 30 μm. Insets in (A, C) show enlargements of the boxed regions, illustrating the closer spacing of boutons in btz mutants.
-
K, LQuantifications of the number of boutons normalized to muscle surface area (×1,000) in the indicated genotypes. ****P < 0.0001; ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; ns, not significant by unpaired t‐test with Welch’s correction. n = 23 (w; da‐GAL4, btz/Df), n = 6 (btz/+), n = 10 (Df/+, UAS‐BtzGFP/+; btz/Df), n = 8 (btz/Df), n = 22 (da>btz‐GFP; btz/Df), n = 13 (BG380‐GAL4; btz/Df; BG380+24B>Btz‐GFP; btz/Df; da‐GAL4/+), n = 5 (BG380>Btz‐GFP; btz/Df), n = 11 (24B‐GAL4; btz/Df; da>btz RNAi), n = 12 (24B>Btz‐GFP; btz/Df; btz RNAi/+), n = 9 (BG380+24B‐GAL4; btz/Df), n = 15 (BG380‐GAL4/+), n = 14 (BG380>btz RNAi; repo>btz RNAi), n = 16 (mhc‐GAL4/+), n = 28 (mhc>btz RNAi), or n = 21 (repo‐GAL4/+). Error bars show mean ± SEM. NMJ size is reduced in btz mutants and rescued by expressing UAS‐btz with da‐GAL4 or with the combination of the BG380‐GAL4 and 24B‐GAL4 drivers, but not with any single driver. Expressing UAS‐btz RNAi with da‐GAL4 or in motor neurons with BG380‐GAL4, muscles with mhc‐GAL4, or glia with repo‐GAL4 also reduces NMJ size.
Source data are available online for this figure.
