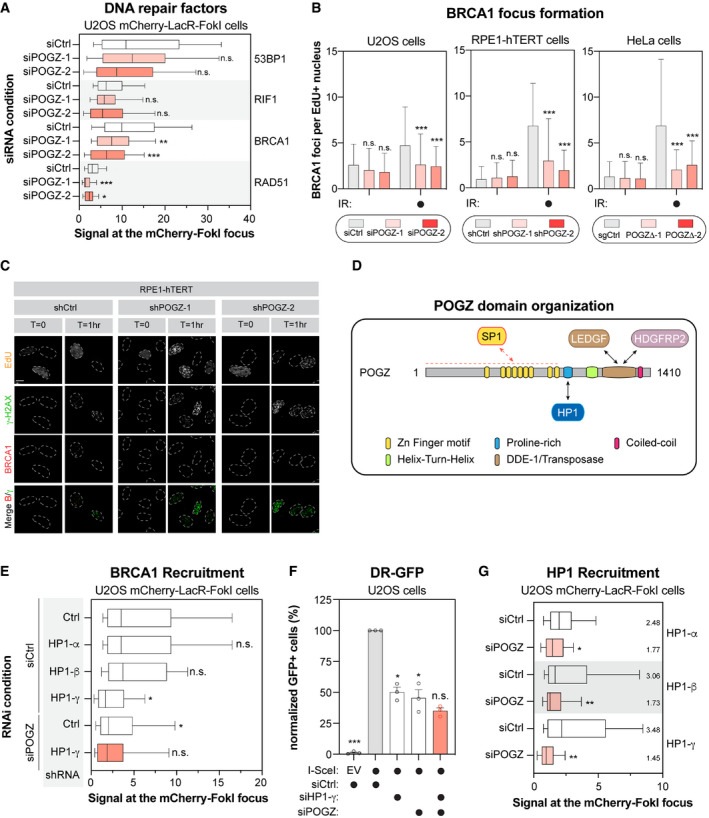
U2OS stably expressing mCherry‐LacR‐FokI were transfected with the indicated siRNA. Twenty‐four hours post‐transfection, DNA damage was induced using Shield1 and 4‐OHT. Immunofluorescence against the indicated DNA repair proteins was subsequently performed to monitor their accumulation at sites of DNA damage by confocal microscopy. Data are represented as a box‐and‐whisker (10–90 percentile) where the fluorescent signal at the mCherry focus was normalized to nuclear background. At least 100 cells per condition were counted (n = 3 biological replicates). Significance was determined by two‐way ANOVA followed by a Dunnett’s test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, **P ≤ 0.0005.
U2OS (left panel), RPE1‐hTERT (middle panel) and HeLa cells (right panel) were monitored for their capacity to form IR‐induced BRCA1 foci. For each cell line, the following conditions were used: U2OS cells were transfected with a non‐targeting siRNA (siCtrl) or an siRNA targeting human POGZ (siPOGZ‐1 or ‐2); RPE1‐hTERT cells were transduced a control shRNA (shCtrl) or a shRNA directed against human POGZ (shPOGZ‐1 or ‐2); HeLa cells were expressing a non‐targeting sgRNA (sgCtrl) or a sgRNA targeting human POGZ and sub‐cloned (POGZΔ‐1 or ‐2). Cells were exposed to 1 Gy before being pulsed with Edu for 1 h and were recovered 1 h post‐exposure to IR. Cells were fixed, stained and imaged via confocal microscopy. Data are the total number of BRCA1 foci in EdU+ cells and represented as a bar graph showing the mean ± SD (n = 3 biological replicates, with at least 100 cells analysed for each time point). Significance was determined by two‐way ANOVA followed by a Dunnett’s test. *P < 0.005, **P < 0.001.
Representative images used for quantification in (B). Scale bar = 5 µm.
Schematic diagram outlining the different domains of human POGZ. Each structural domain and interacting partners are indicated.
U2OS stably expressing mCherry‐LacR‐FokI were transduced with the indicated shRNA and subsequently transfected with the indicated siRNA. Twenty‐four hours post‐transfection, DNA damage was induced using Shield‐1 and 4‐OHT. Immunofluorescence against BRCA1 was subsequently performed to monitor its accumulation at sites of DNA damage by confocal microscopy. Data are represented as a box‐and‐whisker (10–90 percentile) where the fluorescent signal at the mCherry focus was normalized to nuclear background. At least 50 cells per condition were counted. Significance was determined by two‐way ANOVA followed by a Dunnett’s test. *P < 0.0001.
U2OS cells containing the DR‐GFP reporter construct were transfected with the indicated siRNA. Twenty‐four hours post‐transfection. Cells were transfected with the I‐SceI expression plasmid or an empty vector (EV), and the GFP+ population was analysed 48 h post‐plasmid transfection. The percentage of GFP+ cells was determined for each individual condition and subsequently normalized to the non‐targeting condition provided with I‐SceI (siCtrl, I‐SceI). Data are represented as a bar graph showing the relative mean ± SEM, each replicate being representing as a round symbol (n = 3 biological replicates). Significance was determined by one‐way ANOVA followed by a Dunnett’s test. *P ≤ 0.0001.
U2OS stably expressing mCherry‐LacR‐FokI were transduced with the indicated siRNA. Twenty‐four hours post‐transfection, DNA damage was induced using Shield‐1 and 4‐OHT. Immunofluorescence against the indicated HP1 isoform was subsequently performed to monitor its respective accumulation at sites of DNA damage by confocal microscopy. Data are represented as a box‐and‐whisker (10–90 percentile) where the fluorescent signal at the mCherry focus was normalized to nuclear background. At least 75 cells per condition were counted. Significance was determined by two‐way ANOVA followed by a Dunnett’s test. *P < 0.005, **P < 0.0001.