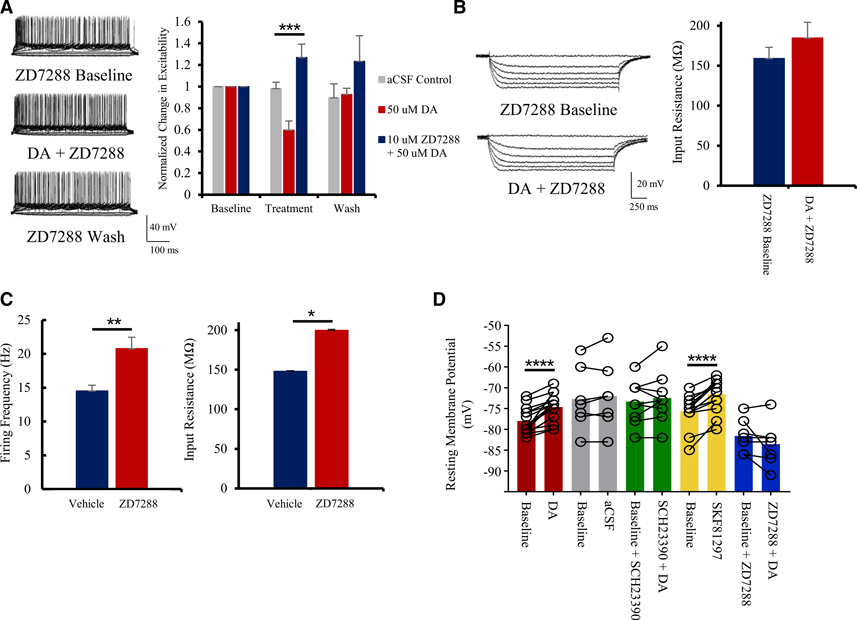
Figure 3. DAergic inhibition depends on HCN channels.
(A) Treatment with the HCN channel blocker 10 μM ZD7288 occludes the inhibitory effects of 50 μM DA. Representative current-clamp traces showing the effects of 10 μM ZD7288 on excitability (left) and group analysis (right; n = 8) are shown.
(B) 10 μM ZD7288 blocks the 50 μM DA-induced decrease in input resistance. Representative current-clamp traces showing the effects of 10 μM ZD7288 on input resistance (left) and quantitative group analysis (right; n = 7) are shown.
(C) Quantitative effects of 10 μM ZD7288 on firing frequency (left) and input resistance (right) at baseline (n = 8).
(D) Both 50 μM DA and 10 μM SKF81297 induce a significant increase in resting membrane potentials of layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons of the ACC. This effect is lost in presence of the D1R antagonist SCH23390 (5 μM) or when HCN channels are blocked with ZD7288 (10 μM; n = 7–17).
Values represented as means ± SEM: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.