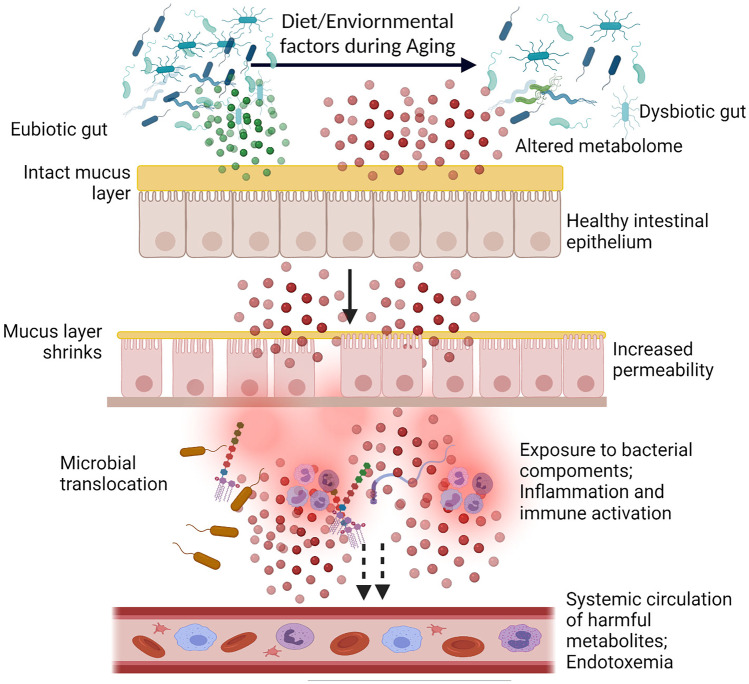
Fig. 2.
Schematic diagram depicting the influence of aging on gut homeostasis. Dominated by diet and environmental factors, aging induces structural and functional changes in the gut microbiota resulting in a dysbiotic gut. The altered metabolome of the dysbiotic gut, shrinkage of the protective mucus layer, and loss of tight junction proteins promote “leakage” through the gut barrier. Bacteria as well as bacterial components, such as LPS and flagella, can translocate through the “leaky gut” and reach lamina propria resulting in activation of immune cells in the Peyer’s patches, and can also cause systemic inflammatory aggravation through peripheral circulation. Illustration created at app.biorender.com