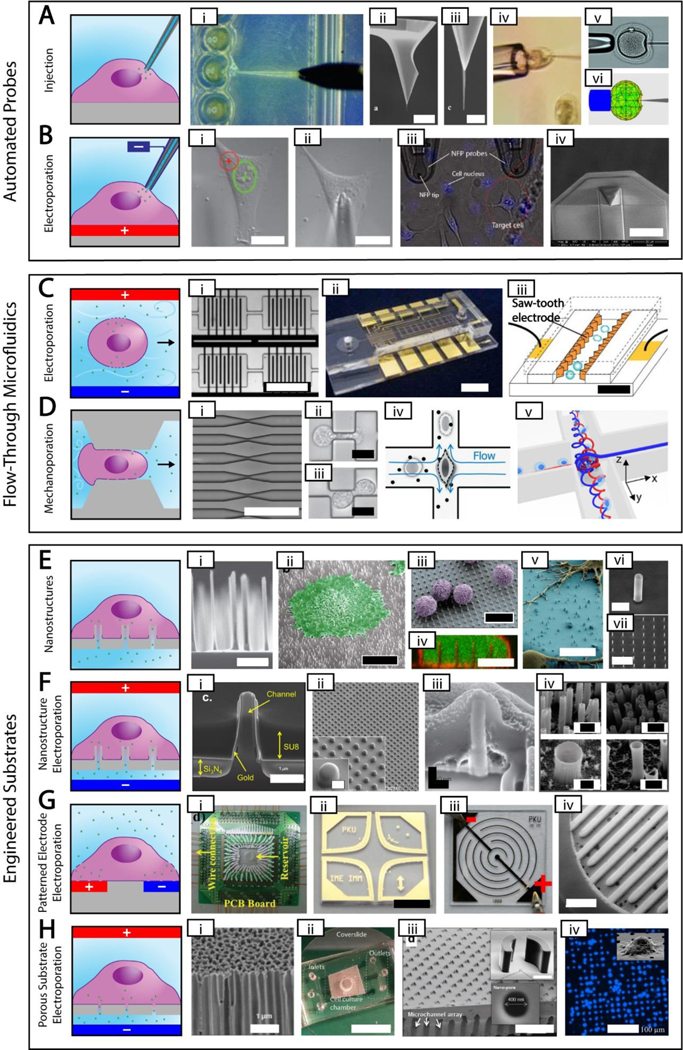
Figure 2. High Throughput, High Control Methods.
Simplified depictions of high throughput, high control methods next to actual images of each method. The electroporation polarities shown are for delivering negative cargos. A. Automated probe-based injection. i. automated injection of zebrafish embryos [87] ii-iii. Different magnifications of an atomic force microscope tip with attached carbon nanotube needle (scale bar = 8 μm and 500 nm, respectively) [48] iv. cell held using a vacuum during injection [50] v-vi. real and simulated deformation during injection (needle diameter = 10 μm) [77] B. Automated probe-based electroporation. i-ii. image processing showing nuclear site in green and cytoplasmic site in red, followed by automated electrode positioning [90] iii. nanofountain probe electroporation (cell size ~ 10–20 μm) [58] iv. An improved version of nanofountain probe using silicon nitride for a soft touch (scale bar = 30 μm) [13]. C. Flow-through microfluidic electroporation. i. vortex microfluidic electroporation (scale bar ~ 720 μm) [97] ii. microfluidic electroporation device (scale bar = 6 mm) [96] iii. sawtooth microfluidic electroporation (scale bar = 40 μm) [95] D. Flow-through microfluidic mechanoporation, including cell squeezing and hydroporation. i. microfluidic constrictions for cell squeezing (scale bar ~ 250 μm) [92] ii-iii. microfluidic constrictions showing single and double deformation, respectively (scale bar = 10 μm) [103] iv. hydrodynamic shearing in hydroporation [105] v. spiral hydroporation [104] E. Nanostructures. i. nanoneedles (scale bar = 2 μm) [110] ii. cell adherent to nanostraws with false color added (scale bar = 10 μm) [121] iii. primary T cells on nanowires with false color added (scale bar = 10 μm) [115] iv. internalized nanowires with the cytoplasm dyed green and the cell membrane dyed red (scale bar = 10 μm) [111] v. neurons adherent to nanowires with false color added (scale bar = 10 μm) [114] vi-vii. silicon nanotubes used for biomolecular cargo delivery (scale bars = 1 um and 10 μm, respectively)[118] G. Patterned electrode electroporation. i. electrode electroporation device with multiple inputs [149] ii. clover electrodes (scale bar = 5 mm) [143] iii. interdigited electrodes [136] iv. 3D interdigited electrodes (scale bar = 800 μm) [141] H. Porous substrate electroporation. i. anodic alumina membrane (scale bar = 1 μm) [155] ii. polycarbonate membrane microfluidic device (scale bar = 12 mm) [153] iii. porous array with nanostructure trapping mechanism (scale bar = 200 μm) [161] iv. DAPI stain showing cell seating on porous array (scale bar = 100 μm) [164]. Permission is needed.