Figure 1. Hyperaccumulation of 22G-RNAs and aberrant gene silencing in prg-1 mutants.
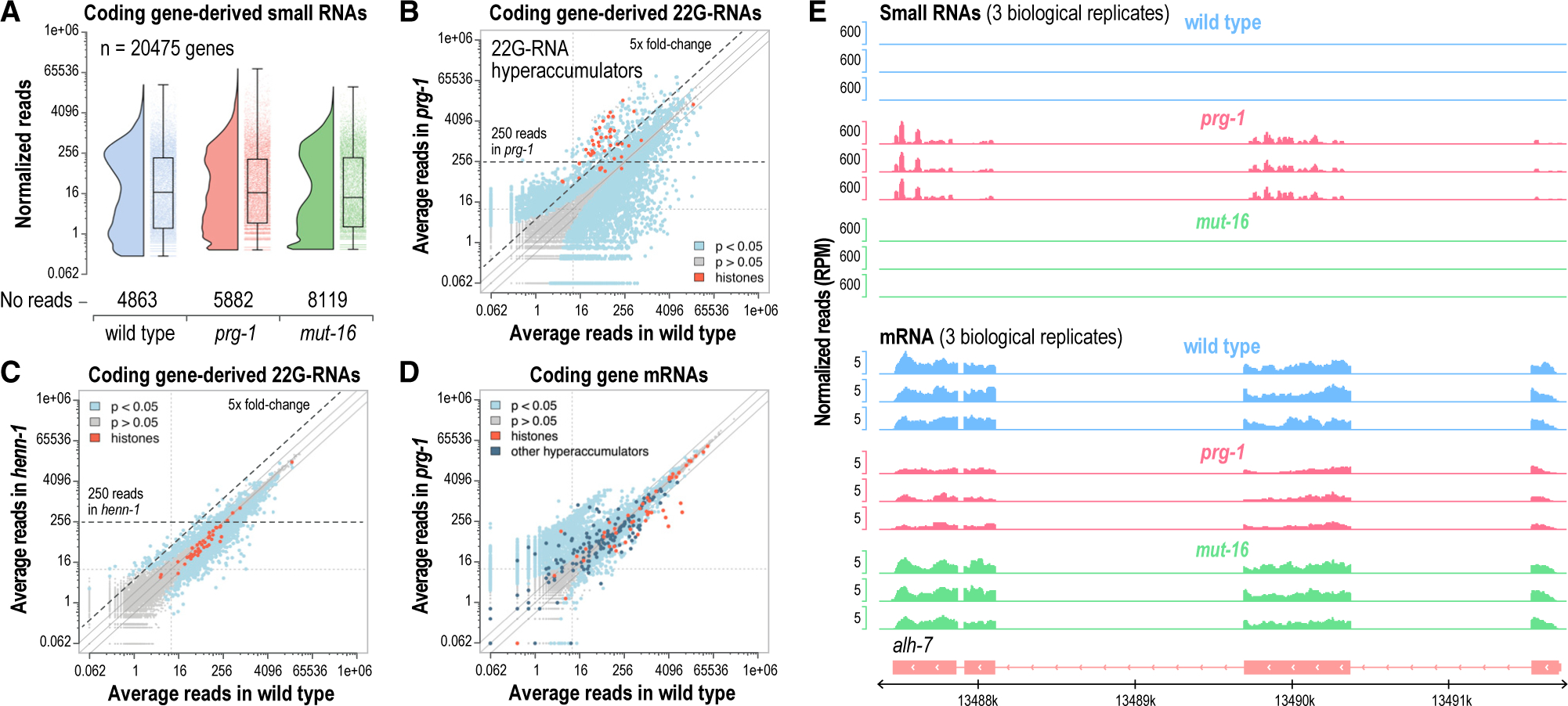
(A) Rain shadow boxplots displaying normalized log2-transformed small RNA high-throughput sequencing reads for each annotated coding gene in dissected distal gonads of wild-type, prg-1(n4357), and mut-16(pk710) mutants (n = 3 biological replicates for each strain). The values on the y axis are reverse transformed to reflect non-transformed values.
(B and C) Scatterplots displaying each gene as a function of normalized log2-transformed small RNA reads in wild-type and prg-1(n4357) (B) or henn-1(pk2295) (C) mutants. The axes are reverse transformed to reflect non-transformed values. Hyperaccumulators are classified as genes that yielded an average of >250 normalized reads and which were upregulated >5-fold in prg-1 mutants, as indicated by the dashed lines. Libraries are from dissected distal gonads (n = 3). Solid lines above and below the y = x lines indicate 2 and −2 fold-changes.
(D) Scatterplot displaying each gene as a function of normalized log2-transformed mRNA high-throughput sequencing reads in wild-type and prg-1(n4357) (axes show non-transformed values).
(E) mRNA and small RNA read distribution across a representative gene locus, alh-7, that hyperaccumulated 22G-RNAs in prg-1 mutants. Three biological replicates are shown for wild-type, prg-1(n4357), and mut-16(pk710).
