Figure 1.
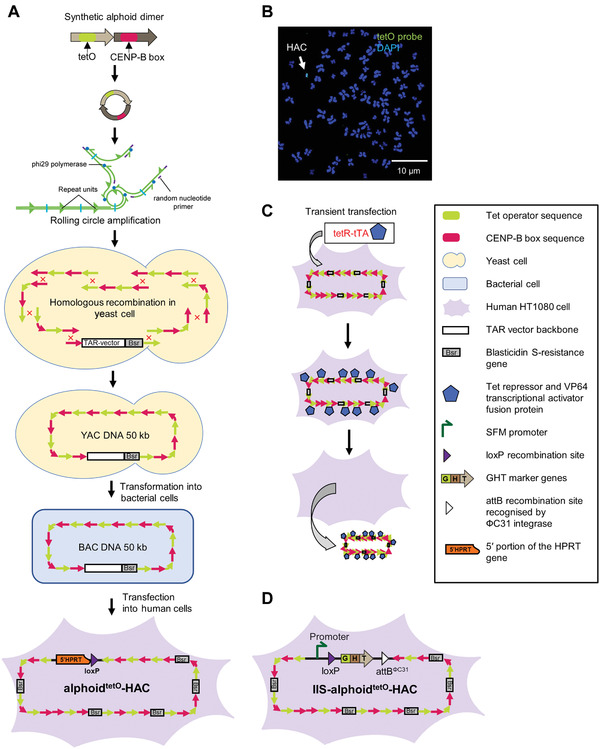
Generation of the alphoidtetO‐HAC using a synthetic alphoid DNA array. (A) A 343‐bp synthetic alphoid dimer consists of two monomers. One monomer is derived from a chromosome 17 alphoid type I 16‐mer unit and contains a CENP‐B box, a nucleotide motif involved in centromere formation. The second monomer is a wholly synthetic sequence derived from alphoid DNA consensus with the sequence corresponding to the CENP‐B box replaced by a 42‐bp tetO motif. A dimer is amplified up to ∼3‐5 kb in size by rolling circle amplification (RCA) in vitro using phi29 DNA polymerase. Then the RCA‐amplified fragments are assembled by transformation‐associated recombination (TAR) cloning in yeast, leading to formation of an ∼50 kb synthetic array cloned into a YAC/BAC vector. A hybrid circular YAC/BAC vector contains a blasticidin resistance marker (a bsr gene). The YAC/BAC molecules are then moved from yeast to bacterial cells for further BAC DNA isolation. After transfection of 50 kb input BAC DNA into human HT1080 cells, the alphoidtetO‐HAC is formed. Formation of the alphoidtetO‐HAC is accompanied by multimerization of input 50 kb DNA up to 1.1 Mb. (B) FISH analysis of the alphoidtetO‐HAC in human HT1080 cells. FISH analysis was performed using a fluorescein peptide nucleic acid (PNA)‐labeled probe for the tetO sequence (see Support Protocol). A white arrow indicates the HAC (green), while the endogenous chromosomes are labeled blue (DAPI). (C) Loss of the alphoidtetO‐HAC from recipient cells may be induced by the transcriptional activator (tTA) fused with the tet‐repressor (tetR) targeting the tetO‐HAC kinetochore (Kim et al., 2011; Kononenko et al., 2014). (D) The IIS‐alphoidtetO‐HAC was developed after insertion of the integration platform cassette into the alphoidtetO‐HAC. The integration platform cassette consists of the SFM promoter driving the expression of the GHT marker, a loxP site present between the promoter and the marker, and the attBΦC31 site for the ΦC31 integrase. The GHT marker is a fusion of enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP), hygromycin‐B‐phosphotransferase (hph), and thymidine kinase (TK). Abbreviations: BAC, bacterial artificial chromosome; YAC, yeast artificial chromosome; HAC, human artificial chromosome; FISH, fluorescence in situ hybridization; SFM, SV40 enhancer plus ferritin; GHT, eGFP‐hph‐TK.
