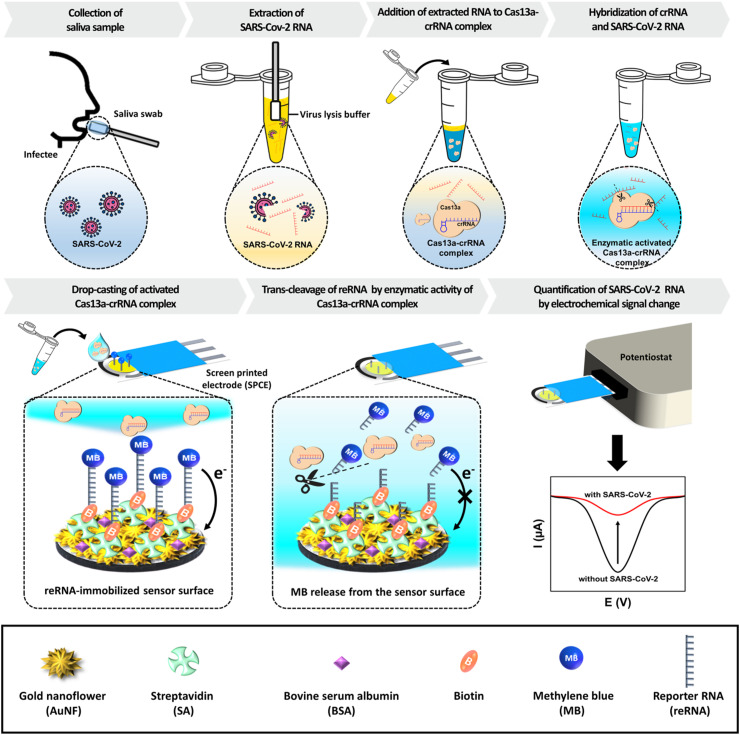
Fig. 1.
Schematic illustration of the proposed electrochemical biosensing strategy utilized with the CRISPR/Cas13a for SARS-CoV-2 detection. Viral RNA is extracted from saliva collected from infected patients using the lysis buffer and mixed with a Cas13a–crRNA complex containing solution. This complex binds with the SARS-CoV-2 RNA, resulting in enzymatic activity. The activated Cas13a–crRNA complex is subsequently loaded onto the sensor surface for cleaving the reRNA immobilized on the electrode. The presence of SARS-CoV-2 can be quantified via analysis of the current change.