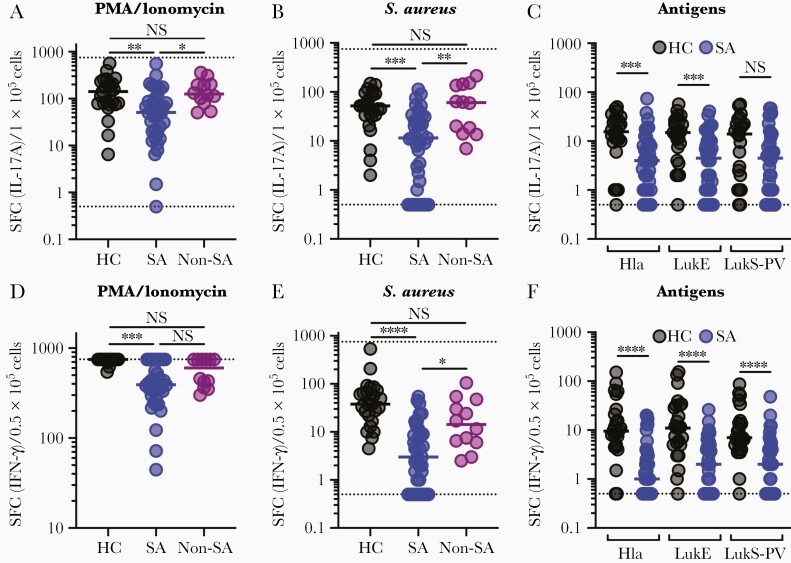
Figure 2.
Effector T-cell responses in healthy and Staphylococcus aureus-infected children. Functional effector T-cell responses were quantified by IL-17A (A–C) or IFN-γ (D–F) ELISpot in thawed PBMCs from 25 healthy children, 39 children with S. aureus infection, and 12 children with an infection not caused by S. aureus. Following culture with PMA and ionomycin, there were impaired IL-17A (A) and IFN-γ (D) responses in children with S. aureus infection compared with healthy controls or children with other infections. Following culture with heat-killed S. aureus, there were markedly impaired IL-17A (B) and IFN-γ (E) responses in infected children compared with healthy children or children with other infections. Following culture with purified Hla, LukE, or LukS-PV, there were markedly impaired IL-17A (C) and IFN-γ (F) responses in infected children. Individual data points are plotted with medians overlaid and distributions were compared using 1-way ANOVA with the Kruskal-Willis post test for multiple comparisons (A, B, D, E) or the Mann-Whitney test (C, F). ** P < .01, *** P < .001, **** P < .0001. The dashed lines indicate the upper (750) and lower (0.5) detectable limits of the assay. Abbreviations: ANOVA, analysis of variance; HC, healthy children; Hla, α-hemolysin; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; IL-17A, interleukin 17A; LukE, leukotoxin E; LukS-PV, Panton-Valentine leucocidin; Non-SA, infection not caused by S. aureus; NS, indicates not significant; PBMCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; PMA, phorbal myristate acetate; SA, S. aureus infection; SFC, spot-forming colonies.