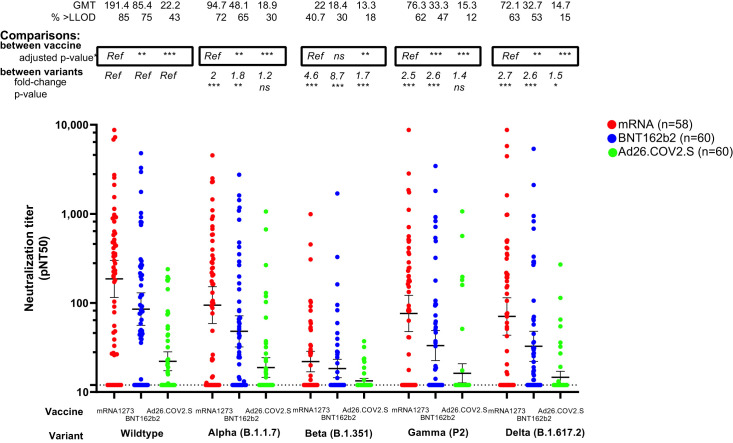
Figure 1.
Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants after vaccination with mRNA1273 (n = 58), BNT162b2 (n = 60), or Ad26.COV2.S (n = 60) in patients with cancer
The y axis shows pseudovirus neutralization titer 50 (pNT50, defined as the titer at which the serum achieves 50% neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 wildtype pseudovirus entry into ACE2-expressing 293T cells).. Briefly, lentiviral particles encoding both luciferase and ZsGreen reporter genes were pseudotyped with the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein from the strain indicated (see Table S1 for sequences) and produced in 293T cells, titered using ZsGreen expression by flow cytometry and used in an automated neutralization assay with 50–250 infectious units of pseudovirus co-incubated with 3-fold serial dilutions of serum for 1 h. Neutralization was determined on 293T-ACE2 cells. A horizontal dotted line is shown at a pNT50 titer of 12, which is the lower limit of detection of this assay; a pNT50 titer of 20 corresponds with the clinical threshold for positivity defined previously (Garcia-Beltran et al., 2021a). The geometric mean titer, proportion positive (at a threshold of 1:12). Statistical comparison of neutralization titers against each strain between recipients of different vaccines is details in Table S2 and denoted by a ∗ on the graph where p value are adjusted for covariates previously shown to be associated with wildtype virus neutralization namely age, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, timing after vaccination, and cancer type. Comparison of neutralization titers for recipients of each vaccine type, against different strains is shown as the fold change in neutralization, and corresponding p value (based on a Dunnet's test conducted in GraphPad Prism v9.0). Horizontal lines denote geometric mean titers, whiskers extend to 2.5th and 97.5th centiles to encompass the 95% CI.