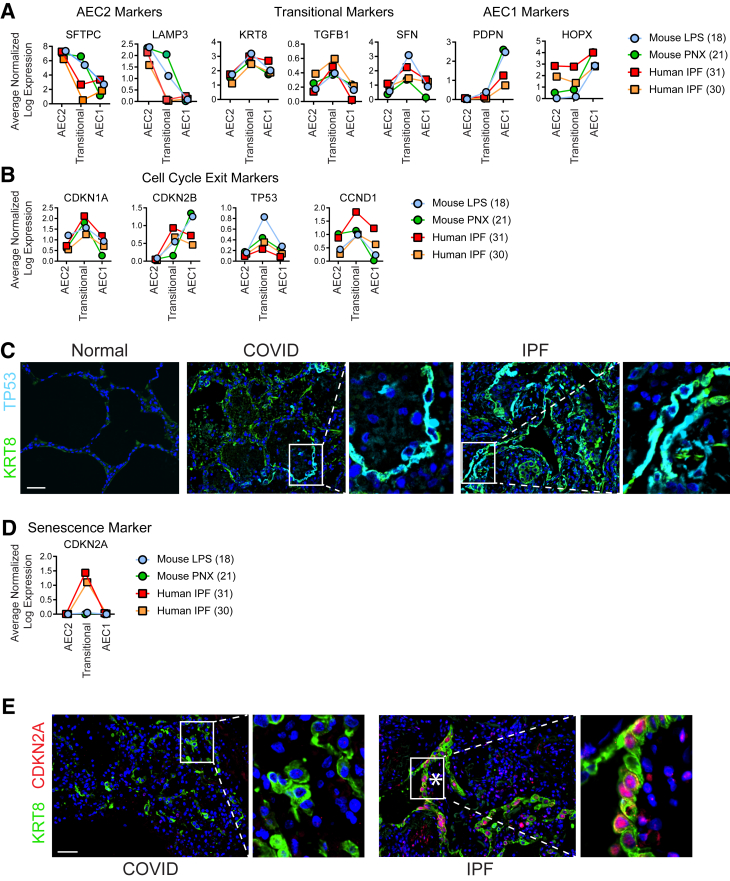
Figure 4.
Transitional cells in mouse models of physiological regeneration, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) acute respiratory distress syndrome, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) exist in a state of cell cycle exit but are senescent only in IPF. A, B, and D: Single-cell RNA sequencing data sets from two mouse models of physiological regeneration, lipopolysaccharide (LPS)18 and pneumonectomy (PNX),21 and human IPF30,31 were interrogated. C and E: Lung sections were immunostained. A: As type 2 alveolar epithelial cells (AEC2s) assume the transitional state, they down-regulate AEC2 markers and up-regulate transitional markers that are conserved in mouse models of physiological regeneration and human IPF. Type 1 AECs (AEC1s) express low levels of transitional markers and high levels of AEC1 markers. In mouse models of physiological regeneration, COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome, and IPF, transitional cells express general markers of cell cycle exit (B and C), but only in IPF do they express CDKN2A/p16, a highly specific marker of senescence (D and E). C and E: Asterisks indicate fibroblastic foci. n = 3. Scale bars = 50 μm. CCND1, cyclin D1; CDKN1A, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A; CDKN2A, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A; CDKN2B, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2B; HOPX, HOP homeobox; KRT8, keratin 8; LAMP3, lysosome-associated membrane glycoprotein 3; PDPN, podoplanin; SFN, stratifin; TGFB1, transforming growth factor-beta 1; TP53, tumor protein P53.