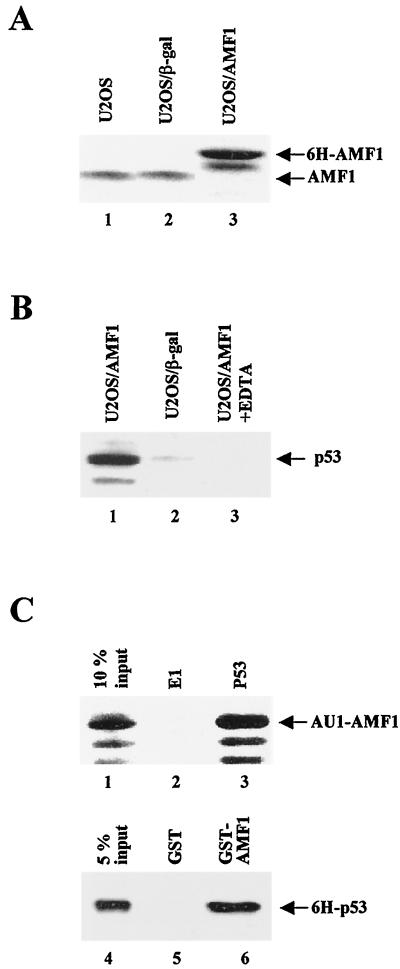
FIG. 2.
In vivo and in vitro complex formation of AMF1 and p53. (A) AMF1 expression in human U2OS cell lines. Equal amounts of total cellular protein extracts from parental U2OS (lane 1), U2OS/β-Gal (lane2), and U2OS/AMF1 (lane 3) cells were subjected to Western blotting with polyclonal rabbit serum against AMF1. (B) U2OS/AMF1 or U2OS/β-Gal cells were treated with 10 μM etoposide for 8 h, extracts were prepared and incubated with Ni-NTA resin in the presence (lane 3) or absence (lanes 1 and 2) of 10 mM EDTA. After extensive washing, six-histidine-tagged proteins were eluted and concentrated. Copurification of p53 with 6H-AMF1 (lane 1) or 6H–β-Gal (lane 2) was probed by Western blotting with MAb DO-1. (C) In vitro binding of AMF1 to p53. (Upper panel) Sf9 cells were infected by recombinant baculoviruses expressing AU1-AMF1, p53, or bovine papillomavirus E1 proteins, harvested 40 h postinfection, and lysed as described previously (54). Cell extract with AU1-AMF1 was incubated with extract containing E1 (lane 2) or p53 (lane 3). P53 was immunoprecipitated with MAb pAb421 and protein A-conjugated Sepharose beads. After washing, the immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blotting with polyclonal antibody against AMF1. Input cell extract (10%) containing AU1-AMF1 was loaded in lane 1. (Lower panel) GST (lane 5) or GST-AMF1 fusion (lane 6) was incubated with 6H-p53 and washed extensively. Bound proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting with MAb DO-1 against p53. Input 6H-p53 (5%) was loaded in lane 4.