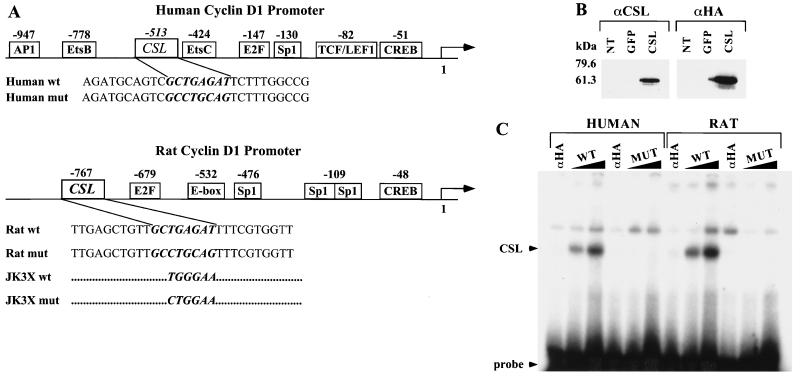
FIG. 5.
Identification of a CSL binding site in the human and rat cyclin D1 promoters. (A) Schematic representation of the human and rat cyclin D1 promoter. The binding sites for transcription factors identified in the cyclin D1 promoter are indicated with their positions relative to the starting site of transcription. The sequences of coding strands of the oligonucleotides used in the EMSA are reported under the schematic representation. In italic and bold is the wt or mut sequence for the CSL binding site identified in the human or the rat cyclin D1 promoter. The JK3X oligonucleotides contain three repeats of the indicated wt or mut consensus sequence for the CSL binding site. The complete sequences for the JK3X oligonucleotides are described in Materials and Methods. (B) Expression of HA-tagged CSL in 293T cells. Cell lysates were prepared from 293T cells not transfected (NT) or transiently transfected with an expression vector encoding GFP (lanes or GFP) the CSL HA-tagged protein (lanes CSL). Protein expression was analyzed by Western immunoblotting using an anti-CSL antibody (αCSL) and an anti-HA tag antibody (αHA). Standard molecular markers are indicated to the left. (C) CSL binds to the sequence identified in the human and rat cyclin D1 promoter. EMSA analysis was performed by incubating increasing amounts (60 and 120 fmol) of the indicated radiolabeled oligonucleotide duplex with 20 μg of lysate extracted from 293T cells expressing HA-tagged CSL. Sixty femtomoles of each oligonucleotide duplex was also incubated with lysates preincubated with the anti-HA probe antibody (lanes αHA). The positions of the CSL-DNA complex and of the free probe are indicated.