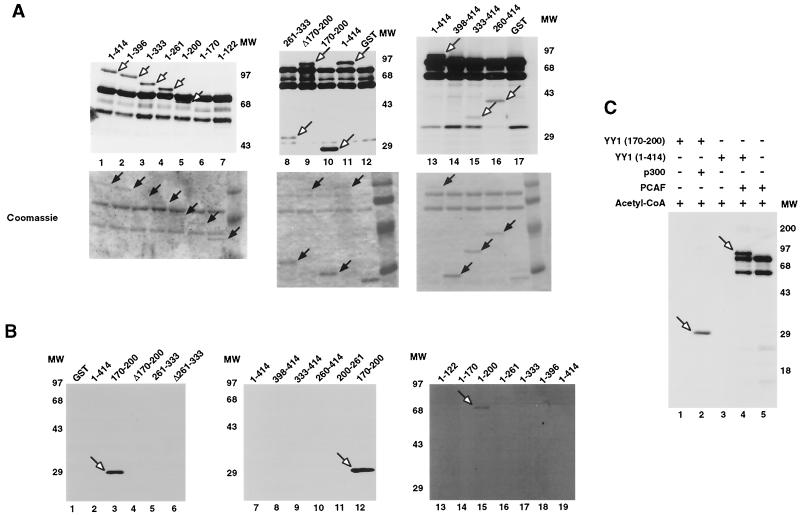
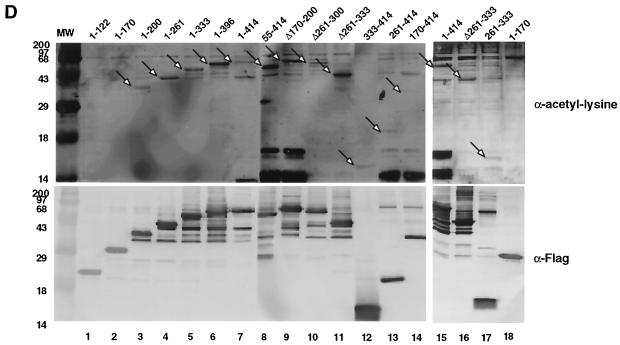
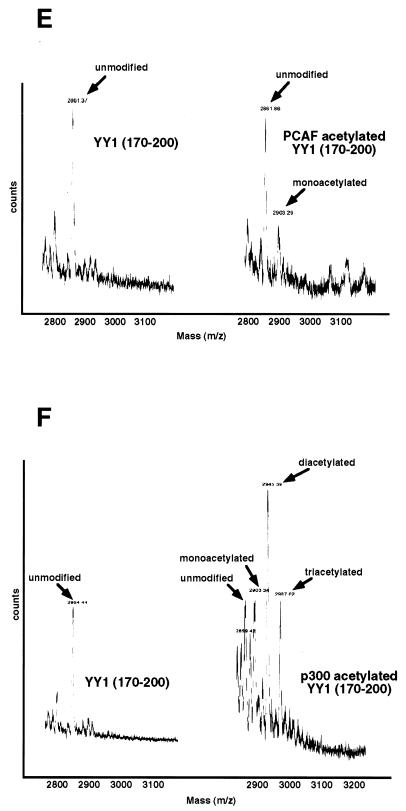
FIG. 2.
Acetylation of YY1 in vitro and in vivo. (A) Acetylation of YY1 by PCAF. Serial GST-YY1 deletion proteins were incubated with GST-PCAF and separated by SDS-PAGE. The gels were then exposed to X-ray film to detect acetylated proteins. Open arrows indicate acetylated YY1 proteins. Auto-acetylated forms of PCAF were detected as three bands of ∼68 kDa. Solid arrows indicate GST-YY1 deletion proteins. (B) Acetylation of YY1 by p300. Serial GST-YY1 deletion proteins were incubated with GST-p300. Arrows indicate YY1 proteins acetylated by p300. (C) Acetylation of YY1 is dependent on p300 or PCAF. In vitro acetylation reactions were performed in the presence or absence of p300 or PCAF. Arrows indicate that YY1 was acetylated only in the presence of p300 or PCAF. (D) Identification of regions of YY1 acetylated in vivo. F-YY1 serial deletion proteins were transiently expressed in HeLa cells, immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody, and analyzed by Western blotting using anti-acetyl lysine antibody and anti-Flag antibody. Arrows indicate immunoprecipitated YY1 proteins that were acetylated. (E and F) Determination of the number of acetylated lysines by mass spectrometry. A YY1 peptide containing residues 170 to 200 was in vitro acetylated by PCAF or p300 and subjected to mass spectrometry analysis. Left panels are spectra from mock-acetylated peptides. Right panels contain spectra from acetylated as well as unacetylated peptides. Small peaks around 3100 m/z in Fig. 2E represent degraded GST-PCAF or background chemical noises.