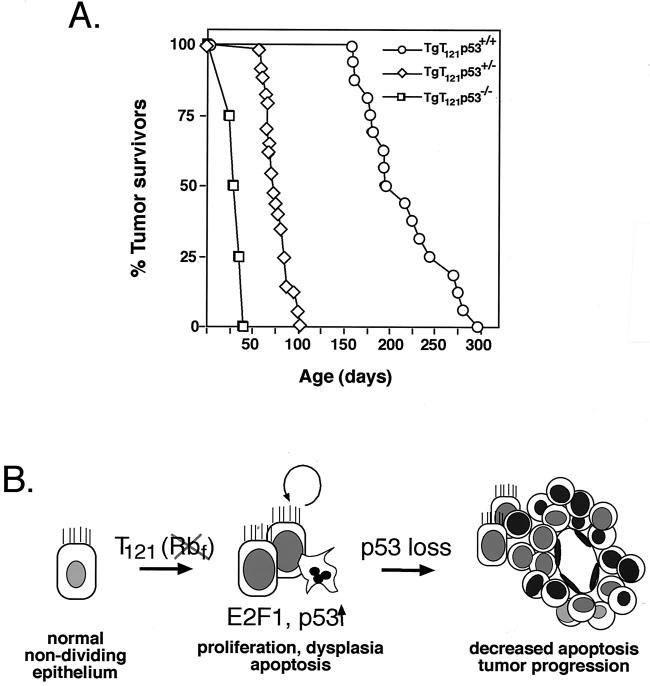
FIG. 1.
A pathway to tumor development. (A) Time of survival from brain tumors depends on p53 status. Mice were sacrificed when they showed severely bulged crania and decreased activity. Histological examination confirmed the presence of CP masses in all mice. (Data are revised from those presented in reference 60.) (B) The diagram depicts previously elucidated steps in T121-induced development of CP tumors. T121 induces proliferation of normally nondividing epithelial cells by inactivating the pRb family proteins pRb, p107, and p130. p53-dependent apoptosis is then activated by a process requiring E2F1 (48). As shown in the present report, in a p53 heterozygous background, the selective pressure for p53 inactivation is 100%, resulting in the focal development of solid vascularized tumors.